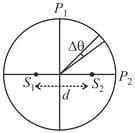
A thin wire is placed between two accurately flat glass plates, creating a wedge of air between the plates. The plates are illuminated with a sodium lamp ( ) and viewed at near-normal incidence. bright fringes are counted over the between the line where the plates are touching and the location of the wire.
(i) Sketch the fringe pattern as seen from above the glass plates (i.e. looking down from the top of the diagram above).
(ii) Calculate the diameter of the wire. You must explain your method - don't just plug numbers into an equation Explain why a dark fringe is observed along the line where the plates are touching.
(iii)Explain why a dark fringe is observed along the line where the plates are touching.
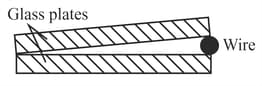
(i) Sketch the fringe pattern as seen from above the glass plates (i.e. looking down from the top of the diagram above).
(ii) Calculate the diameter of the wire. You must explain your method - don't just plug numbers into an equation Explain why a dark fringe is observed along the line where the plates are touching.
(iii)Explain why a dark fringe is observed along the line where the plates are touching.

Important Questions on Wave Optics
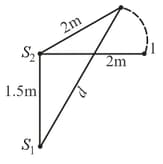
Two coherent sources of sound, and produce sound waves of the same wavelength are in phase. and are placed apart (see fig). A listener, located at , directly in front of , finds that the intensity is at a minimum when he is away from . The listener moves away from , keeping the distance from fixed. The adjacent maximum of intensity is observed when the listener is at a distance from . Then is :
The Young's double slit experiment is performed with blue light and green light of wavelengths and respectively. If is the distance of maxima from the central one, then
Two coherent point sources and are separated by a small distance as shown in the figure. The fringes obtained on the screen will be

In a Young's double slit experiment with light of wavelength the separation of slits is and distance of screen is such that . If the Fringe width is , the distance from point of maximum intensity to the point where intensity falls to half of the maximum intensity on either side is: