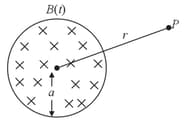
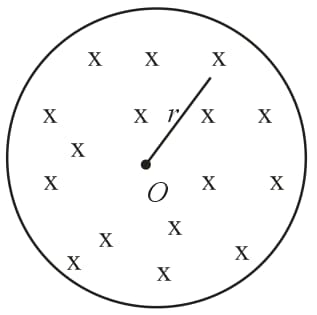
A uniform but time-varying magnetic field exists in a circular region of radius and is directed into the plane of the paper as shown. The magnitude of the induced electric field at point (outside the circular region) at a distance from the centre of the circular region
Important Questions on Electromagnetic Induction
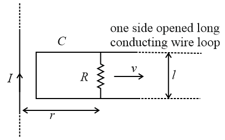
An infinitely long straight wire carrying current , one side opened rectangular loop and a conductor with a sliding connector are located in the same plane, as shown in the figure. The connector has length and resistance . It slides to the right with a velocity . The resistance of the conductor and the self-inductance of the loop are negligible. The induced current in the loop, as a function of separation , between the connector and the straight wire is:
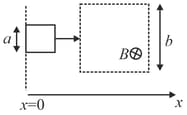
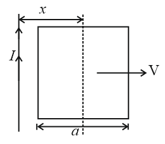
A square-shaped conducting wire loop of dimension a moving parallel to the -axis approaches a square region of size where a uniform magnetic field exists pointing into the plane of the paper (see figure). As the loop passes through this region, the plot correctly depicting its speed as a function of is.
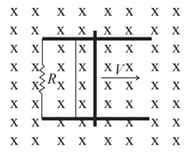
Then, the
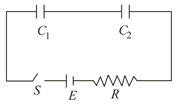
In the following circuit the switch is closed at . The charge on the capacitor as a function of time will be given by
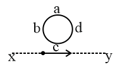
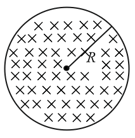
The figure shows a circular area of tthe radius where a uniform magnetic field is going into the plane of the paper and increasing in magnitude at a constant rate. In that case, which of the following graphs, drawn schematically, correctly shows the variation of the induced electric field ?
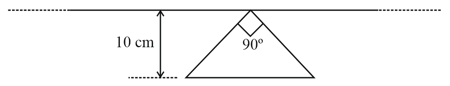
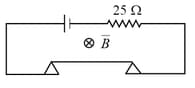
A long thin metal bar of negligible resistance weighing rests on two metal supports as shown in the figure. The supports are connected in series to an ideal cell and a resistance. A uniform magnetic field is applied in the region normal to the plane of the paper and into the paper. Maximum emf that the cell can have without breaking the circuit in volt is
(Acceleration due to gravity )
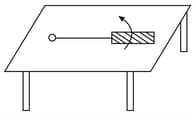
A metallic rod of length is tied to a string of length and made to rotate with angular speed on a horizontal table with one end of the string fixed. If there is a vertical magnetic field B in the region, the e.m.f. induced across the ends of the rod is:
The figure shows the cross section of a cylindrical region of radius in which the magnetic field points into the page. The magnitude of the field is at time and it decreases to zero in seconds.
The induced electric field at a distance from the centre inside the cylindrical region is given by
The circular wire in figure below encircles solenoid in which the magnetic flux is increasing at a constant rate out of the plane of the page.
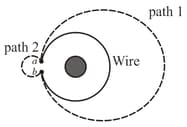
The clockwise emf around the circular loop is By definition a voltammeter measures the voltage difference between the two points given
by We assume that and are infinitesimally close to each other. The values of along the path and along the path respectively are

