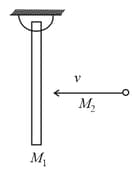
A uniform rod of mass is hinged at its upper end as shown in the figure. A particle of mass which is moving horizontally strikes the rod elastically at its midpoint. If the particle comes to rest after collision, then if the value of what is the value of ?
Important Questions on Rotational Mechanics
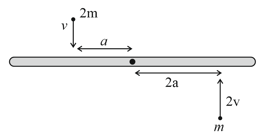
A rigid uniform rod of mass and length is resting on a smooth horizontal table. It is pivoted at its centre. Two marbles each of mass moving with uniform speed in the plane of the table collide with the two ends of the rod simultaneously as shown in the figure. The marbles stuck to the rod and continue to move with the rod. Time taken by the rod to rotate through an angle radian is (in seconds)
A bullet of mass is fired horizontally into a large sphere of mass and radius resting on a smooth horizontal table.
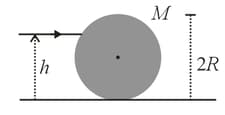
The bullet hits the sphere at a height from the table and sticks to its surface. If the sphere starts rolling without slippng immediately on impact, then
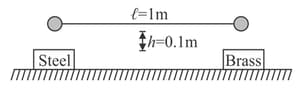
Two steel balls of equal diameter are connected by a rigid bar of negligible weight as shown and are dropped in the horizontal position from height above the heavy steel and brass base plates. If the coefficient of restitution between the ball and steel base is and that between the other ball and the brass base is . The angular velocity of the bar immediately after the rebound is where is: (Assume the two impacts are simultaneous.)
A meter stick weighing is pivoted at its upper end in such a way that it can freely rotate in a vertical plane through this end (shown in the figure). A particle of mass is attached to the upper end of the stick through a light string of length . Initially, the rod is kept vertical and the string horizontal when the system is released from rest. The particle collides with the lower end of the stick and sticks there. Find the maximum angle through which the stick will rise.
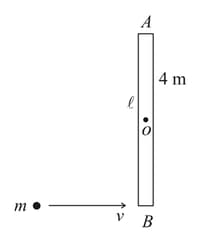
A uniform rod of length and mass lies on a frictionless horizontal surface on which it is free to move anyway. A ball of mass moving with speed as shown in the figure. It collides with the rod at one of the ends. If the ball comes to rest immediately after collision then find out the angular velocity of the rod just after the collision.
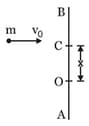
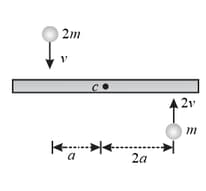
A uniform bar of length and mass lies on a smooth horizontal table. Two point masses and , moving in the same horizontal plane with speed and , respectively, strike the bar (as shown in the figure) and stick to it after collision. Denoting angular velocity (about the centre of mass), total energy and velocity of centre of mass by , and , respectively, after collision, which of the following options is incorrect?
A small disc and a thin uniform rod, of length whose mass is times greater than the mass of the disc, lie on a smooth horizontal plane. The disc is set in motion, in horizontal direction and perpendicular to the rod, with velocity , after which it elastically collides with the end of the rod. Find the velocity of the disc and the angular velocity of the rod, after the collision. At what value of , will the velocity of the disc, after the collision, be equal to zero? Reverse its direction?
A small ball is projected from point P towards a vertical wall as shown in figure. It hits the wall when its velocity is horizontal. Ball reaches point P after one bounce on the floor. The coefficient of restitution assuming it to be same for two collisions is All surfaces are smooth. Find the value of
Represent the union of two sets by Venn diagram for each of the following.
is a prime number between and
is an odd number between and
A stick of length and mass lies on a frictionless horizontal surface on which it is free to move in anyway. A ball of mass moving with speed as shown in fig. Mass of the ball so that it remains at rest immediately after collision is The value of is.
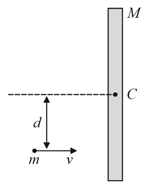
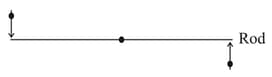
A mass is moving at speed perpendicular to a rod of length and mass which pivots around a frictionless axle running through its centre. It strikes and sticks to the end of the rod. The moment of inertia of the rod about its centre is . Then the angular speed of the system just after the collision is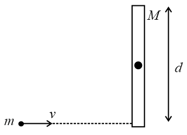
A uniform smooth rod (mass and length ) placed on a smooth horizontal floor is hit by a particle (mass ) moving on the floor, at a distance from one end elastically (). The distance travelled by the centre of the rod after the collision, when it has completed three revolutions, will be
A uniform rod of mass and length is lying on a horizontal table. Two point masses and moving with speed and respectively strike the rod and stick to it as shown in the figure. Kinetic energy of the system after collision is given by The value of is