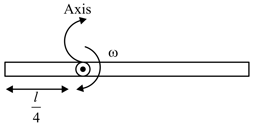
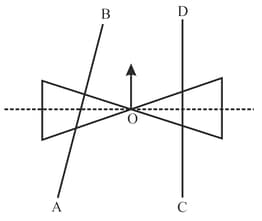
A uniform rod rotates in a vertical plane about the shown axis. Angular velocity at the moment is . Then, force on the rod by the axis at the moment

Important Questions on Rotational Mechanics
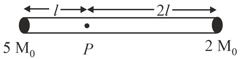
A rigid massless rod of length has two masses attached at each end as shown in the figure. The rod is pivoted at point on the horizontal axis. When released from the initial horizontal position, its instantaneous angular acceleration will be
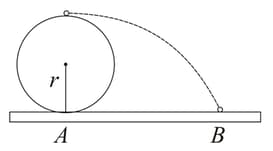
A wheel of radius "rolls without slipping with a speed on a horizontal road. When it is at a point on the road a small bob of the mud separates from wheel at the highest point and touches the point on the road as shown in the figure. Then is (g-acceleration due to gravity)
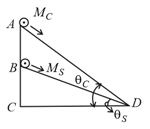
A solid sphere and solid cylinder of identical radii approach an incline with the same linear velocity (see figure). Both roll without slipping all throughout. The two climb maximum heights and on the incline. The ratio is given by:

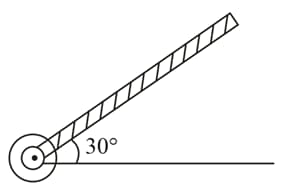
A rod of length is pivoted at one end. It is raised such that it makes an angle of from the horizontal as shown and released from rest. Its angular speed when it passes through the horizontal (in ) will be