A uniform solid sphere of radius produces a gravitational acceleration of on its surface. The distance of the point from the centre of the sphere where the gravitational acceleration becomes is,
Important Questions on Gravitation
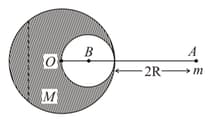
A solid sphere of radius gravitationally attracts a particle placed at from its centre with a force Now a spherical cavity of radius is made in the sphere (as shown in figure) and the force becomes . The value of is:
(Ignore the rotation and revolution of the Earth and the presence of any other planet)
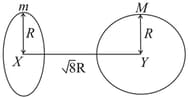
Find the gravitational force of attraction between the ring and sphere as shown in the diagram, where the plane of the ring is perpendicular to the line joining the centres. If is the distance between the centres of a ring (of mass ) and a sphere (mass ) where both have equal radius
Inside a uniform spherical shell :
(a) The gravitational field is zero.
(b) The gravitational potential is zero.
(c) The gravitational field is the same everywhere.
(d) The gravitation potential is the same everywhere.
(e) All the above.
Choose the most appropriate answer from the options given below:
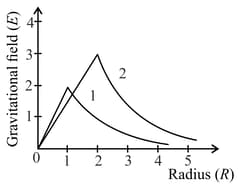
Consider two solid spheres of radii , and masses and respectively. The gravitational field due to sphere and are shown. The value of is: