A vertical cylinder closed from both ends is equipped with an easily moving piston dividing the volume into two parts, each containing one mole of air. In equilibrium at the volume of the upper part is times greater than that of the lower part. At what temperature will the ratio of these volumes be equal to

Important Questions on THERMODYNAMICS AND MOLECULAR PHYSICS
A vessel of volume is evacuated by means of a piston air pump. One piston stroke captures the volume . How many strokes are needed to reduce the pressure in the vessel times? The process is assumed to be isothermal and the gas, ideal.
Find the pressure of air in a vessel being evacuated as a function of evacuation time . The vessel's volume is and initial pressure is The process is assumed to be isothermal and the evacuation rate equal to , and independent of pressure.
Note: The evacuation rate is the gas volume being evacuated per unit time, with that volume being measured under the gas pressure attained by that moment.
A chamber of volume is evacuated by a pump, whose evacuation rate equals . How soon will the pressure in the chamber decrease by times?
Given that , where, is the pressure as a function of time.
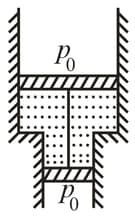
A smooth vertical tube, having two different sections, is open from both ends and equipped with two pistons of different areas. Each piston slides within a respective tube section. One mole of ideal gas is enclosed between the pistons tied with a non-stretchable thread. The cross-sectional area of the upper piston is , greater than that of the lower one. The combined mass of the two pistons is equal to . The outside air pressure is . By how many must the gas between the pistons be heated, to shift the pistons through ?
Find the maximum attainable temperature of an ideal gas, in each of the following processes,
(a) ,
(b) ,
where, and are the positive constants and is the volume of one mole of gas.
