MEDIUM
JEE Advanced
IMPORTANT
Earn 100
A voltmeter has a resistance of ohm and range volt. The value of resistance used in series to convert it into voltmeter of range volt is
(a)
(b)
(c)
(d)
50% studentsanswered this correctly

Important Questions on Electrical Measuring Instruments
MEDIUM
JEE Advanced
IMPORTANT
A galvanometer has a resistance of . A shunt is connected across it such that of the total current passes through the galvanometer. The value of the shunt is,
MEDIUM
JEE Advanced
IMPORTANT
In previous question, the combined resistance of the shunt and the galvanometer is,
Previous question
A galvanometer has a resistance of . A shunt is connected across it such that of the total current passes through the galvanometer. The value of the shunt isHARD
JEE Advanced
IMPORTANT
A galvanometer has a resistance of . A shunt is connected across it such that of the total current in main circuit passes through the galvanometer. The external resistance that must be connected in series with the main circuit, so that the total current in the main circuit remains unaltered before and after the galvanometer is shunted is,
MEDIUM
JEE Advanced
IMPORTANT
An ammeter is obtained by shunting a galvanometer with a resistance. What additional shunt should be connected across it to double the range?
EASY
JEE Advanced
IMPORTANT
The voltmeters are connected as shown.
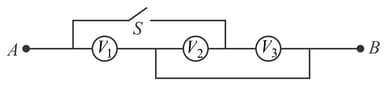
A potential difference has been applied between and . On closing the switch , readings of voltmeters?
MEDIUM
JEE Advanced
IMPORTANT
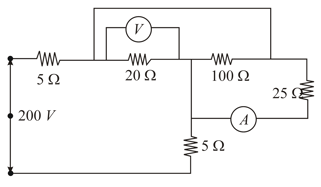
In figure, the voltmeter and ammeter shown are ideal. Then voltmeter and ammeter readings, respectively, are
EASY
JEE Advanced
IMPORTANT
A potentiometer arrangement is shown in the figure. The driver cell has emf and internal resistance .
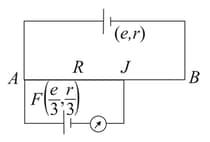
The resistance of potentiometer wire is . is the cell of emf and internal resistance . Balance point () can be obtained for all finite values of
MEDIUM
JEE Advanced
IMPORTANT
When a galvanometer is shunted with a resistance, the deflection is reduced to . If the galvanometer is further shunted with a wire, the new deflection will be (assuming the main current remains the same),
