A wire carrying a current is placed at right angles to a uniform magnetic field of magnetic flux density. When the current in the wire is / , the magnetic force that acts on the wire is .
What is the force on the wire, placed in the same orientation, when the magnetic field strength is and the current is
A B C D

Important Questions on Magnetic Fields and Electromagnetism
There is an electric current in a wire of mass per unit length• The wire is placed in a magnetic field of strength T and the current is gradually increased until the wire just lifts off the ground. What is the value of the current when this happens?
A current-carrying wire is placed in a uniform magnetic field.
(a) Describe how the wire should be placed to experience the
maximum force due to the magnetic field.
A current-carrying wire is placed in a uniform magnetic field.
(b) Describe how the wire should be placed to experience no force due to the magnetic field .
A current-carrying conductor placed at right angles to a uniform magnetic field experiences a force of Determine the force on the wire when, separately:
(a) the current in the wire is increased by a factor of
A current-carrying conductor placed at right angles to a uniform magnetic field experiences a force of Determine the force on the wire when, separately:
(b) the magne tic flux density is halved
A current-carrying conductor placed at right angles to a uniform magnetic field experiences a force of Determine the force on the wire when, separately:
(c) the length of the wire in the magnetic field is reduced to
of its original length.
A copper wire carrying a current of has of its length placed in a uniform magnetic field, as shown.
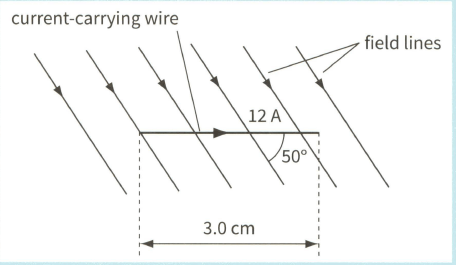
The force experienced by the wire is when the angle between the wire and the magnetic field is
(a) Calculate the magnetic flux density.
A copper wire carrying a current of has of its length placed in a uniform magnetic field, as shown.
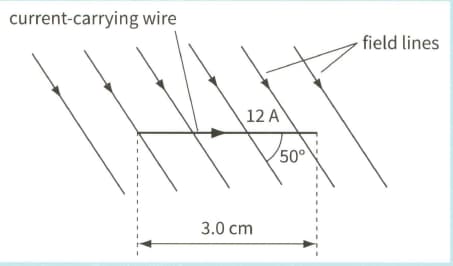
The force experienced by the wire iswhen the angle between
the wire and the magnetic field is
(b) State the direction of the force experienced by the wire.
