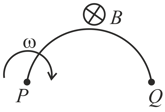
A wire is bent to form a semicircle of radius . The wire rotates about its one end with angular velocity . Axis of rotation being perpendicular to the plane of the semicircle. In the space, a uniform magnetic field of induction exists along the axis of rotation, as shown in figure. Then
Important Questions on Electromagnetic Induction
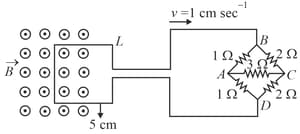
A rod of length slides with a speed of on a rectangular conducting frame as shown in figure. There exists a uniform magnetic field of perpendicular to the plane of the figure. If the resistance of the rod is . The current through the rod is
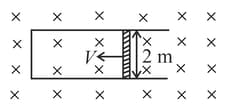
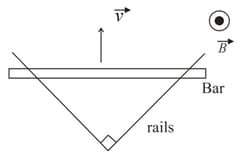
Consider the situation given in figure. The wire slides on the fixed rails with a constant velocity. If the wire is replaced by a semicircular wire, the magnitude of the induced current will:
A metallic rod of length is tied to a string of length and made to rotate with angular speed on a horizontal table with one end of the string fixed. If there is a vertical magnetic field B in the region, the e.m.f. induced across the ends of the rod is:
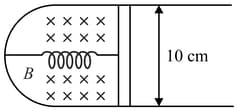
A thin strip long is on a shaped wire of negligible resistance and it is connected to a spring of spring constant (see figure). The assembly is kept in a uniform magnetic field of If the strip is pulled from its equilibrium position and released, the number of oscillations it performs before its amplitude decreases by a factor of is . If the mass of the strip is grams, its resistance and air drag negligible, will be close to:
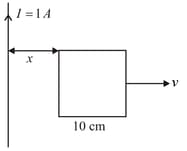
A square frame of side and a long straight wire carrying current are in the plane of the paper. Starting from close to the wire, the frame moves towards the right with a constant speed of (see figure). The e.m.f induced at the time the left arm of the frame is at from the wire is
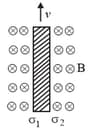
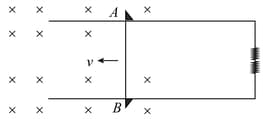
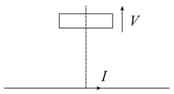
As shown in the figure, a rectangular loop of a conducting wire is moving away with a constant velocity in a perpendicular direction from a very long straight conductor carrying a steady current . When the breadth of the rectangular loop is very small compared to its distance from the straight conductor, how does the emf: induced in the loop vary with time
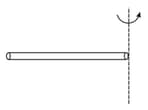
A horizontal rod of length rotates about a vertical axis with a uniform angular velocity . A uniform magnetic field exists parallel to the axis of rotation. Then potential difference between the two ends of the rod is
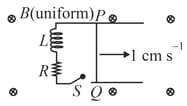
[Assume the velocity of wire remains constant after key is closed. Given: where is base of the natural logarithm]