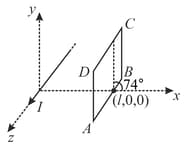
A wire of infinite length carrying current lies along the z-axis. A square loop of side is placed such that the plane of the loop makes an angle with the positive axis at and side touches the axis and parallel to axis as shown in the figure. The magnetic flux passing through the loop is . Find the value of . [take and ]

Important Questions on Electromagnetic Induction and Alternating Current
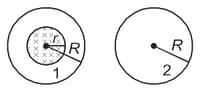

An emf in the coil will be generated for the following situations.
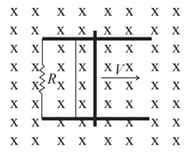
Then, the
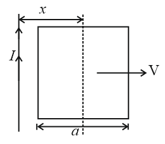
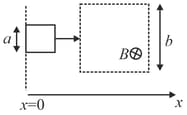
A square-shaped conducting wire loop of dimension a moving parallel to the -axis approaches a square region of size where a uniform magnetic field exists pointing into the plane of the paper (see figure). As the loop passes through this region, the plot correctly depicting its speed as a function of is.
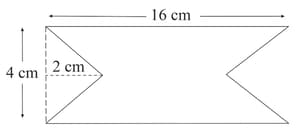
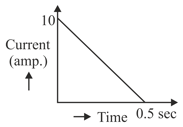
In a coil of resistance , a current is induced by changing the magnetic flux through it as shown in the figure. The magnitude of change in flux through the coil is: