ADH, insulin and glucagon are hormones that control aspects of homeostasis. ADH is a short peptide, glucagon is a single polypeptide and insulin is composed of two polypeptides. The target cells for these hormones only respond if they have specific cell surface receptors.
Explain why the target cells for ADH, insulin and glucagon must have cell surface receptors in order for them to respond.

Important Questions on Control and Coordination
ADH, insulin and glucagon are hormones that control aspects of homeostasis. ADH is a short peptide, glucagon is a single polypeptide and insulin is composed of two polypeptides. The target cells for these hormones only respond if they have specific cell surface receptors.
State the target cells for each of these hormones.
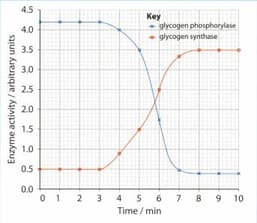
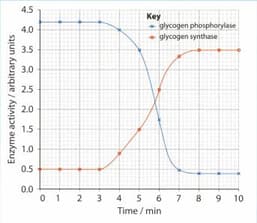
Two intracellular enzymes that are involved with the synthesis and breakdown of glycogen in liver cells are glycogen synthase and glycogen phosphorylase. Liver cells were exposed to a solution with a high concentration of glucose. The activity of the two enzymes was determined at intervals for 10 minutes. The graph shows the results.
Two intracellular enzymes that are involved with the synthesis and breakdown of glycogen in liver cells are glycogen synthase and glycogen phosphorylase. Liver cells were exposed to a solution with a high concentration of glucose. The activity of the two enzymes was determined at intervals for 10 minutes. The graph shows the results.
State what happens to the quantity of glycogen stored in a liver cell between 4 minutes and 10 minutes.
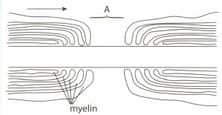
The given drawing was made from a TEM of an LS through a myelinated neurone.
Name the region of the neurone labelled A.