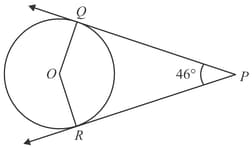
According to the converse of alternate segment theorem "If a line is drawn through an end point of a chord of a circle so that the angle formed with the chord is equal to the angle subtended by the chord in the alternate segment, then the line is a tangent to the circle"
Important Questions on Circle and Tangents
How many tangents can be drawn on the circle from a point outside the circle?
Suppose are two unequal circles; and are the direct common tangents to these circles. A transverse common tangent cuts in and in . If units, then is -
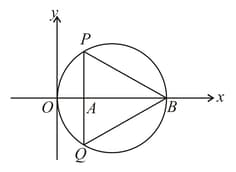
On the circle with center , points are such that . A point is located on the tangent at to the circle such that and are on the opposite sides of the line and . The line segment intersects the circle again at . Then the ratio is equal to -
At one end of a diameter of a circle of radius , tangent is drawn to the circle. The length of the chord parallel to and at a distance from is
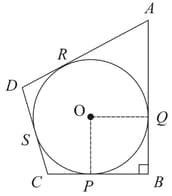
In the figure below, a circle with centre is inscribed in a quadrilateral such that, it touches sides , , and at points , , and respectively. If , and then the radius of the circle (in ) is
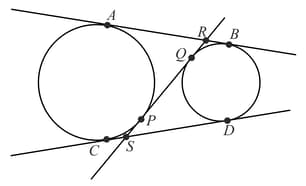
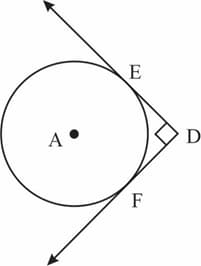
Two circles touch each other externally at . is a common tangent to the circle touching them at and . Then value of is
In a right triangle , right-angled at and The radius of the circle inscribed in the triangle (in ) is
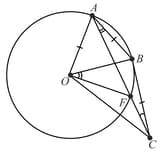
In the figure below, and are tangents from an external point to a circle with centre . If and then the radius of the circle is
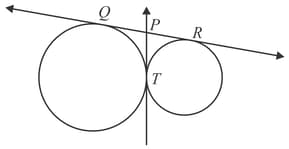
In Fig., is a common tangent to the given circles touching externally at the point . The tangent at meets at . If then the length of (in ) is
In the figure, and are two tangents to a circle with centre . If then is