EASY
Diploma
IMPORTANT
Earn 100
Amino acids can exist in and forms. Describe how the form of alanine, , differs in its physical properties from the form.

Important Questions on Biochemistry
EASY
Diploma
IMPORTANT
EASY
Diploma
IMPORTANT
EASY
Diploma
IMPORTANT
EASY
Diploma
IMPORTANT
EASY
Diploma
IMPORTANT
EASY
Diploma
IMPORTANT
The structures of vitamin and the preservatives and are shown in figure .
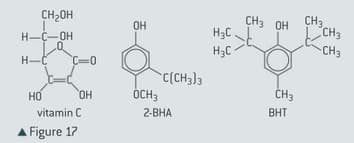
Determine any chiral carbon atoms in these three compounds by placing an asterisk, *, beside them on a copy of the figure.
EASY
Diploma
IMPORTANT
EASY
Diploma
IMPORTANT
