Ammonia, , is a weak base. It has a value of .
Calculate the pH of a aqueous solution of ammonia at .

Important Questions on Acids and Bases (AHL)
Distinguish between the terms strong and weak acid and state the equations used to show the dissociation of acids and in aqueous solution.
Ammonia can be converted into nitric acid, , and hydrocyanic acid, . The of hydrocyanic acid is .
Deduce the expression for the ionization constant, , of hydrocyanic acid and calculate its value from the value given.
Ammonia can be converted into nitric acid, , and hydrocyanic acid, . The of hydrocyanic acid is .
Calculate the and the of an aqueous solution of hydrocyanic acid of concentration . State one assumption made in arriving at your answer.
of ammonia, , was dissolved in water to make of solution. This solution has a hydroxide ion concentration of . Determine the of the solution.
of ammonia, , was dissolved in water to make of solution. This solution has a hydroxide ion concentration of . Calculate the base dissociation constant, , for ammonia.
Consider an acid–base indicator solution.
What is the effect on this acid–base indicator when sodium hydroxide solution is added to it?
The graph below shows the titration curve of of of hydrochloric acid with sodium hydroxide, of concentration. The indicator methyl orange was used to determine the equivalence point. Methyl orange has a pH range of .
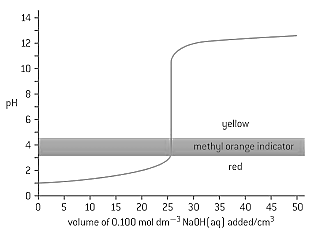
If the hydrochloric acid was replaced by ethanoic acid of the same volume and concentration, which property of the titration would remain the same?
