An alternating emf source with a variable frequency is connected in series with a resistor and a capacitor. The emf amplitude is .
(a) Draw a phasor diagram for phasor (the potential across the resistor) and phasor (the potential across the capacitor).
(b) At what driving frequency do the two phasors have the same length?
At that driving frequency, what are
(c) the phasor angle in degrees,
(d) the angular speed at which the phasors rotate, and
(e) the current amplitude?
(c) the phasor angle in degrees,

Important Questions on Electromagnetic Oscillations and Alternating Current
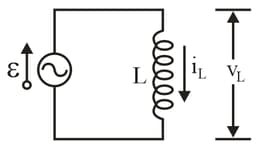
A inductor is connected as in the figure, to an generator with . What is the amplitude of the resulting alternating current if the frequency of the emf is
and ?
If is (), what is with an open circuit? If the secondary now has a resistive load of What is the current in the
primary and secondary?
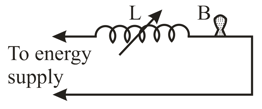
A typical light dimmer used to dim the stage lights in a theater consists of a variable inductor (whose inductance is adjustable between zero and ) connected in series with a light bulb , as shown in figure. The electrical supply is () at The light bulb is rated at .
(a) What is required if the rate of energy dissipation in the light bulb is to be varied by a factor of from its upper limit of ? Assume that the resistance of the light bulb is independent of its temperature.
(b) Could one use a variable resistor (adjustable between zero and instead of an inductor?
(c) If so, what is required?
(d) Why isn't this done?
In a certain oscillating circuit, the total energy is converted from electrical energy in the capacitor to magnetic energy in the inductor in s.
What are
(a) The period of oscillation and
(b) The frequency of oscillation?
(c) How long after the magnetic energy is a maximum will it be a maximum again?
(d) In one full cycle, how many times will the electrical energy be maximum?
