An astronaut rotates at the end of the test machine whose arm has a length of , as shown in the diagram. The acceleration she experiences must not exceed .
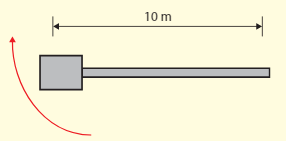
Determine the maximum number of revolutions per minute of the arm.


Important Questions on Circular Motion and Gravitation
A body of mass is tied to a string and rotates on a horizontal, frictionless table.
a. The length of the string is and the speed of revolution is . Calculate the tension in the string.
A body of mass is tied to a string and rotates on a horizontal, frictionless table. The length of the string is .
b. The string breaks when the tension exceeds . Determine the largest speed the mass can rotate at?
A body of mass is tied to a string and rotates on a horizontal, frictionless table.
c. The breaking tension of the string is but you want the mass to rotate at . Determine the shortest length string that can be used.
A neutron star has a radius of and completes one revolution every .
a. Calculate the centripetal acceleration experienced at the equator of the star.
A neutron star has a radius of and complete one revolution every .
b. The acceleration of free fall at the surface of the star is . State and explain whether a probe that landed on the star could stay on the surface or whether it would be thrown off.
The earth rotates around the Sun in an orbit that is approximately circular, with a radius of .
a. Estimate the orbital speed of the earth around the sun.
The earth rotates around the Sun in an orbit that is approximately circular, with a radius of .
b. Determine the centripetal acceleration experienced by the earth.
