MEDIUM
Earn 100
An electron in an atom revolves around the nucleus in an orbit of radius . Calculate the equivalent magnetic moment, if the frequency of revolution of electron is . ()
Important Questions on Moving Charges and Magnetism
EASY
A magnetic dipole is acted upon by two magnetic fields which are inclined to each other at an angle of . One of the fields has a magnitude of . The dipole attains stable equilibrium at an angle of with this field. The magnitude of the other field (in ) is close to
MEDIUM
A rectangular coil of length and width having turns of wire is suspended vertically in a uniform magnetic field of strength . The coil carries a current of . If the plane of the coil is inclined at an angle of with the direction of the field, the torque required to keep coil in stable equilibrium will be:
MEDIUM
The dipole moment of a circular loop carrying a current I, is m and the magnetic field at the centre of the loop is . When the dipole moment is doubled by keeping the current constant, the magnetic field at the centre of the loop is . The ratio is:
EASY
Torque acting on a rectangular coil carrying current situated parallel to magnetic field of induction , having the number of turns and area is
EASY
Obtain an expression for magnetic moment of an orbital electron.
EASY
Following figures show the arrangement of bar magnets in different configurations. Each magnet has magnetic dipole Which configuration has highest net magnetic dipole moment?
EASY
The magnetic moment of electron due to orbital motion is proportional to ( = principal quantum numbers)
EASY
The ratio of angular momentum to the atomic dipole moment for hydrogen like atoms and ions is
EASY
A charge is spread uniformly over an insulated loop of radius . If it is rotated with an angular velocity with respect to normal axis then magnetic moment of the loop is:
EASY
The magnetic moments associated with two closely wound circular coils and of radius respectively are equal if: (Where are number of turn and current of respectively)
MEDIUM
An iron rod of volume and relative permeability is placed as core in a solenoid with . If a current of is passed through the solenoid, then the magnetic moment of the rod will be :
EASY
Magnetic moment of revolving electron of charge and mass in terms of angular momentum of electron is
EASY
A wire of length metre carrying a current of ampere is bent in the form of a circle. Its magnetic moment is,
EASY
A square loop is carrying a steady current and the magnitude of its magnetic dipole moment is . If this square loop is changed to a circular loop and it carries the same current, the magnitude of the magnetic dipole moment of circular loop will be:
MEDIUM
A coil in the shape of an equilateral triangle of side is suspended between the pole pieces of a permanent magnet such that is in plane of the coil. If due to a current in the triangle, a torque rests on it, the side of the triangle is
EASY
The ratio of the magnetic field at the centre of a current-carrying circular coil to magnetic moment is . If the current and the radius both are doubled. The new ratio will become
EASY
In a permanent magnet at room temperature
HARD
A rectangular loop of sides and , carrying a current of , is placed in different orientations as shown in the figure below.
(a) 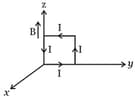 (b)
(b) 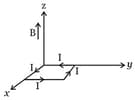
(c) 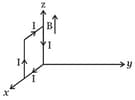 (d)
(d) 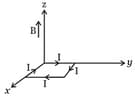
If there is a uniform magnetic field of in the positive direction, in which orientations the loop would be in stable equilibrium and unstable equilibrium?
HARD
Derive an expression for magnitude of magnetic dipole moment of a revolving electron. A circular coil of turns and diameter carries a current of . Calculate the magnitude of the magnetic dipole moment associated with the coil.
MEDIUM
A proton is revolving on a circular path of radius with frequency . Magnetic dipole moment associated with proton is

