An element (atomic number ) reacts with an element (atomic number ) to form a divalent halide.
Where in the periodic table are elements and placed?

Important Questions on Periodic Classification of Elements
An element (atomic number ) reacts with an element (atomic number ) to form a divalent halide.
Classify and as metal (s), non-metal (s) or metalloid (s).
An element (atomic number ) reacts with an element (atomic number ) to form a divalent halide.
What will be the nature of oxide of element ? Identify the nature of bonding in the compound formed?
An element (atomic number ) reacts with an element (atomic number ) to form a divalent halide.
Draw the electron dot structure of the divalent halide.
Atomic number of a few elements are given below
(a) Identify the elements.
(b) Identify the group number of these elements in the periodic table.
(c) Identify the periods of these elements in the periodic table.
(d) What would be the electronic configuration for each of these elements?
(e) Determine the valency of these elements.
Complete the following crossword puzzle (Figure).
Across
An element with atomic number
Metal used in making cans and member of group
A lustrous non-metal which has electrons in its outermost shell.
Down
Highly reactive and soft metal which impacts yellow colour when subjected to flame and is kept kerosene.
The first element of second period.
An element which is used in making fluorescent bulbs and is second member of group in the modern periodic table.
A radioactive element which is the last member of halogen family.
Metal which is an important constituent of steel and forms rust when exposed to moist air.
The first metalloid in modern periodic table whose fibers are use in making bullet-proof vests.
In this ladder (Figure) symbols of elements are jumbled up. Rearrange these symbols of elements in the increasing order of their atomic numbers in the periodic table.
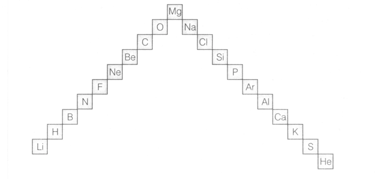
In this ladder (Figure) symbols of elements are jumbled up. Arrange the elements in the order of their group.
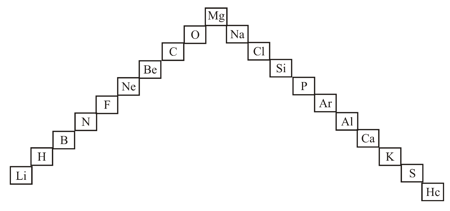
.
Mendeleev predicted the existence of certain elements not known at that time and named two of them as Eka-silicon and Eka-aluminium.
(a) Name the elements which have taken the place of these elements.
