EASY
Earn 100
An ideal gas expands from an initial volume into vacuum under isothermal conditions. For this process.
(a) and
(b) and
(c) and
(d) and
28.57% studentsanswered this correctly
Important Questions on Chemical Thermodynamics
MEDIUM
EASY
How much heat will be absorbed by mole of an ideal gas, if it is expanded reversibly from to at ?
HARD
HARD
MEDIUM
The combination of plots which does not represent isothermal expansion of an ideal gas is
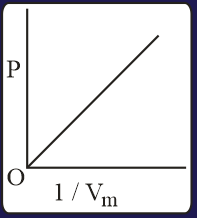
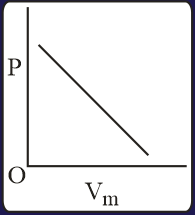
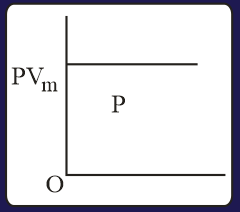
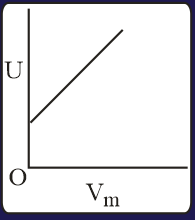
EASY
EASY
MEDIUM
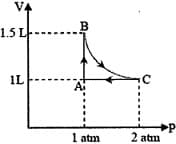
EASY
EASY
Under the isothermal condition, a gas at expands from to against a constant external pressure of bar. The work done by the gas is
(Given that bar)
EASY
MEDIUM
HARD
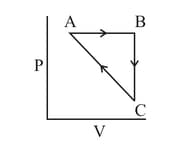
Heat absorbed by the system during process is
MEDIUM
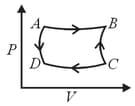
and are isothermal processes while and are adiabatic processes. The same cycle in the temperature - entropy plane is :
HARD
EASY
HARD
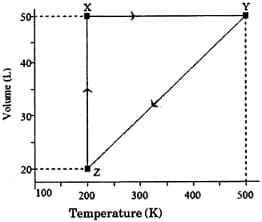
The pressure of the gas (in atm) at and respectively, are
EASY
HARD
HARD
(Given,