An isolated system is that which can exchange energy but not matter with the surroundings.
Important Questions on Thermodynamics
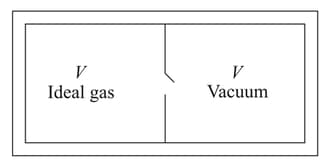
Consider the given diagram. An ideal gas is contained in a chamber (left) of volume and is at an absolute temperature It is allowed to rush freely into the right chamber of volume which is initially vacuum. The whole system is thermally isolated. What will be the final temperature, if the equilibrium has been attained?
Consider the following thermodynamical variables
(i) Pressure
(ii) Internal Energy
(iii) Volume
(iv) Temperature
Out of these, the intensive variable(s) is (are)
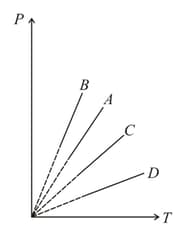
Pressure versus temperature graph of an ideal gas at constant volume is shown by the straight-line . Now mass of the gas is doubled and the volume is halved then the corresponding pressure versus temperature graph will be shown by the line
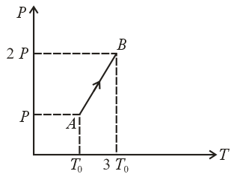
The pressure versus temperature graph of an ideal gas is shown in the figure below. If the density of gas at point is , then the density of the gas at point will be
Three different processes that can occur in an ideal monoatomic gas are shown in the vs diagram. The paths are labelled as and . The change in internal energies during these process are taken as and and the work done as and . The correct relation between these parameters are:
Some of the thermodynamic parameters are state variables while some are process variables. Some grouping of the parameters are given. Choose the correct one
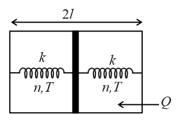
The left part is in contact with a thermostat (a device which maintains a constant temperature). When an amount of heat Q is supplied to the gas in the right part, the piston is displaced to the left by a distance x = ℓ/2. Determine the heat Q' given away to the thermostat by the left part of the piston.