An object is placed (from the reflecting surface) in front of a block of glass thick having its farther side silvered. The final image is formed at behind the silvered face. The refractive index of glass is

Important Questions on Ray Optics
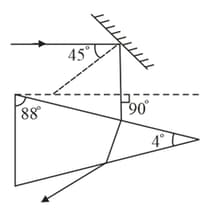
A ray of light strikes a plane mirror at an angle of incidence as shown in the figure. After reflection, the ray passes through a prism of refractive index , whose apex angle is . The angle through which the mirror should be rotated if the total deviation of the ray is to be is
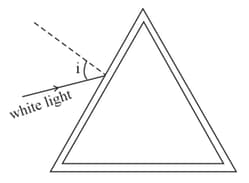
A beam of white light is incident on the hollow prism of glass as shown in the figure. Then
Two plane mirrors of length are separated by distance and a man is standing at a distance from the connecting line of mirrors as shown in the figure. A man is walking in a straight line at a distance parallel to mirrors at speed , then the man at will be able to see an image of for the time
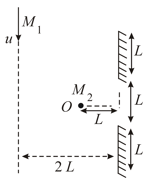
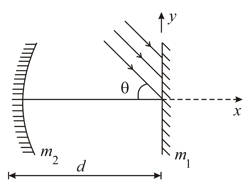
In the figure shown a thin parallel beam of light is incident on a plane mirror at a small angle . is a concave mirror of focal length . After three successive reflections of this beam, the and coordinates of the image is
The distance between an object and its doubly magnified image by a concave mirror is
[Assume focal length]
In the figure shown, the image of a real object is formed at the point . is the principal axis of the mirror. The mirror must be
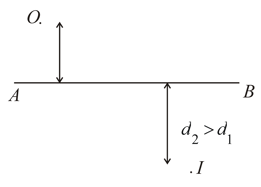
In the shown figure and are two concave mirrors of the same focal length . and are their principal axes, respectively. A point object is kept on the line at a distance from . The distance between the mirrors is . Considering two successive reflections first on and then on . The distance of the final image from the line is
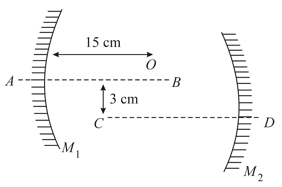
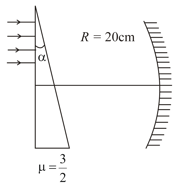
In the given figure a parallel beam of light is incident on the upper part of a prism of angle and R.I. . The light coming out of the prism falls on a concave mirror of radius of curvature . The distance of the point (where the rays are focused after reflection from the mirror) from the principal axis is