Assertion: A lighter and a heavier bodies moving with same moment and experiencing same retarding force have equal stopping times.
Reason: For a given force and momentum, stopping time is independent of mass.
Important Questions on Force and Laws of Motion
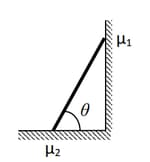
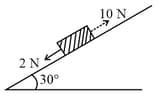
The values of the coefficient of friction and the distance , are respectively close to:
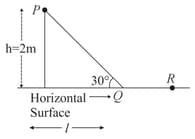
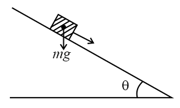
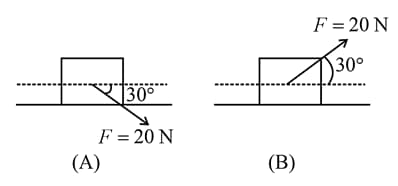
A block of mass is (i) pushed in case and (ii) pulled in case by a force making an angle of with the horizontal, as shown in the figures. The coefficient of friction between the block and floor is The difference between the accelerations of the block, in case and case will be:
A block of mass is kept against an accelerating wedge with a wedge angle of to the horizontal. The co-efficient of friction between the block and the wedge is . What is the minimum absolute value of the acceleration of the wedge to keep the block steady. Assume
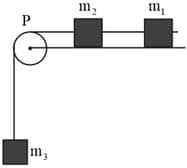
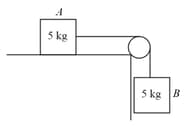
A block of mass resting on a horizontal surface is connected by a cord, passing over a light frictionless pulley to a hanging block of mass . The coefficient of kinetic friction between the block and the surface is . Tension in the cord is
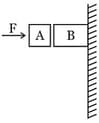
Given in the figure are two blocks and of weight and , respectively. These are being pressed against a wall by a force and kept in equilibrium as shown. If the coefficient of friction between the blocks is and between block and the wall is , the frictional force applied by the wall on block is:

