Assertion: We have a solid charged sphere. There are two points and is a point lying between centre and surface of the sphere. is at finite and non-zero distance from the surface outside the sphere. There will be no situation where electric potential is equal at and .
Reason: Rate of change of electric field with distance from centre merely represents, magnitude of electric potential at that point.

Important Questions on Electrostatics
Assertion: Cyclotron is used to accelerate heavy charged particles, such as a proton. It is not suitable for accelerating light charged particles such as electrons.
Reason: Specific charge of a proton is more than compared to the electron.
Reason: Net electrostatic potential at the centre is zero.
Assertion: Inside a solid charged sphere variation is linear.
Reason: Inside that solid charged sphere variation is parabolic.
Assertion: Two charges each are fixed at two points. If a third charge is placed at centre, then this charge is in stable equilibrium condition line joining the charges.
Reason: Electrostatic potential energy of the system in this position is minimum.
Assertion: Two concentric spherical shells and are charged by charges and . If is negative, then is also negative.
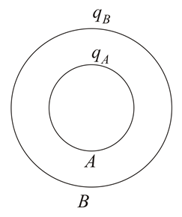
Reason: . Therefore, if is negative, then is also negative.
Assertion: Two identical balls are charged by . They are suspended from a common point by two insulating threads each. In equilibrium, the angle between the threads is . (Ignore gravity)
Reason: In equilibrium tension in the springs is
Assertion: With the help of Gauss theorem, we can find electric field at any point.
Reason: Gauss theorem can be applied for any type of charge distribution.
Assertion: When a capacitor is charged by a battery half of the energy supplied by the battery is stored in the capacitor and the rest half is lost.
Reason: If resistance in the circuit is zero, then there will be no loss of energy.
