At what altitude above the Earth's surface would the gravitational acceleration be ?

Important Questions on Gravitation
An asteroid, whose mass is times the mass of the Earth, revolves in a circular orbit around the Sun at a distance that is times Earth's distance from the Sun. Calculate the period of revolution of the asteroid in . What is the ratio of kinetic energy of the asteroid to the kinetic energy of Earth?
In , the spacecraft Galileo sent an image of asteroid and a tiny orbiting Moon (now known as Dactyl), the first confirmed example of an asteroid-Moon system. In the image, the moon, which is wide, is away from the centre of the asteroid, which is long. Assume the Moon's orbit is circular with a period of . What is the mass of the asteroid? The volume of the asteroid, measured from the Galileo images, is What is the density (mass per unit volume) of the asteroid?
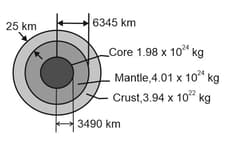
In the figure shown, not to scale, a cross-section through the interior of the Earth rather than being uniform throughout, the Earth is divided into three zones: an outer crust, a mantle, and an inner core. The dimensions of these zones and the masses contained within them are shown in the figure. The Earth has a total mass of and a radius of Ignore rotation and assume that Earth is spherical.
Calculate at the surface.
Suppose that a borehole (the mole) is driven to the crust-mantle interface at a depth of what would be the value of at the bottom of the hole?
Suppose that the Earth were a uniform sphere, with the same total mass and size. What would be the value of at a depth of (Precise measurements of are sensitive probes of the interior structure of the Earth, although results can be clouded by local variations in mass distribution).
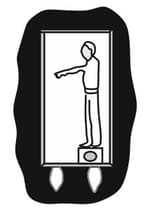
In the figure shown below, the scale on which the physicist stands reads . How long will the cantaloupe take to reach the floor if the physicist drops it (from rest relative to himself) at a height of above the floor?