Below is a flow chart for the Contact process:
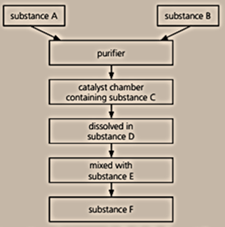
Name the substances A, B, C, D, E, and F.


Important Questions on Some Non-Metals and their Compounds
Below is a flow chart for the Contact process:
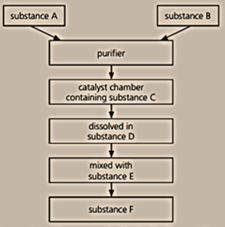
Why is a catalyst used?
Below is a flow chart for the Contact process:
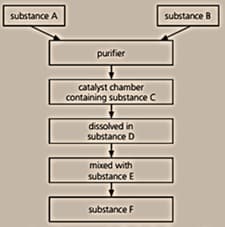
Write a chemical equation for the reaction that takes place on the catalyst.
Below is a flow chart for the Contact process:
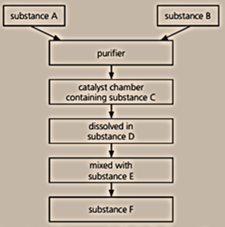
The production of substance F is very important. Why? Give three reasons.
Below is a flow chart for the Contact process:
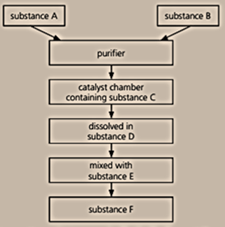
Copy out the flow chart, and write in the full names of the different substances.
Dilute sulfuric acid has typical acid properties. An excess of it is added to test tubes W, X, Y and Z, which contain these powdered substances:
W. Copper oxide
X. Magnesium
Y. Calcium hydroxide
Z. Sodium carbonate
In which test-tubes will you observe fizzing?
Dilute sulfuric acid has typical acid properties. An excess of it is added to test tubes W, X, Y and Z, which contain these powdered substances:
W. Copper oxide
X. Magnesium
Y. Calcium hydroxide
Z. Sodium carbonate
In which test-tube will a coloured solution form?
Dilute sulfuric acid has typical acid properties. An excess of it is added to test tubes W, X, Y and Z, which contain these powdered substances:
W. Copper oxide
X. Magnesium
Y. Calcium hydroxide
Z. Sodium carbonate
In which of the test-tubes does neutralisation take place?
Dilute sulfuric acid has typical acid properties. An excess of it is added to test tubes W, X, Y and Z, which contain these powdered substances:
W. Copper oxide
X. Magnesium
Y. Calcium hydroxide
Z. Sodium carbonate
Name the four salts obtained, after reaction.
