EASY
Earn 100
Brief account of Ionic equilibria.
Important Questions on Ionic Equilibria
HARD
Differentiate between the following pair based on the information given in the brackets.
- Conductor and electrolyte (conducting particles)
EASY
Write short note on following-
Weak Electrolyte
EASY
HARD
EASY
MEDIUM
EASY
Write short note on following-
Strong Electrolyte
EASY
EASY
An electrolyte which completely dissociates into ions is:
EASY
MEDIUM
EASY
EASY
EASY
EASY
MEDIUM
HARD
For which of the following solute, plot is:
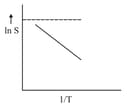
when represents the enthalpy of the solution?
EASY
MEDIUM

