By means of plotting, find
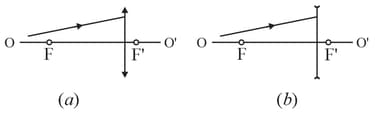
the path of a ray of light beyond thin converging and diverging lenses (where is the optical axis, and are the front and rear focal points);
the position of a thin lens and its focal points, if the position of the optical axis and the positions of the conjugate points (see figure) are known; the media on both sides of the lenses are identical;
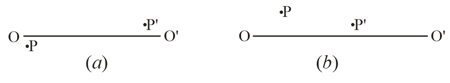
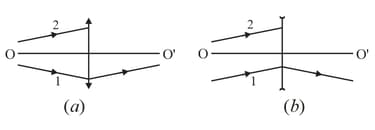
the path of ray beyond the converging and diverging lenses (Figure), if the path of ray and the positions of the lens and of its optical axis are all known; the media on both sides of the lenses are identical.

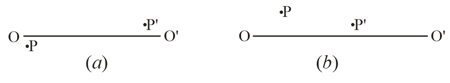


Important Questions on OPTICS
the distance between the two positions of the lens is ,
the transverse dimensions of the image at one position of the lens are greater than those at the other position.
Figure illustrates an aligned system consisting of three thin lenses. The system is located in air. Determine,
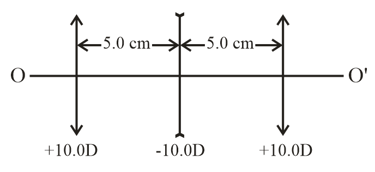
the position of the point of convergence of a parallel ray incoming from the left after passing through the system,
the distance between the first lens and a point lying on the axis to the left of the system, at which that point and its image are located symmetrically with respect to the lens system.
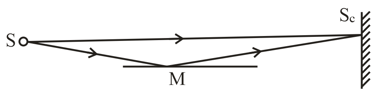
In Lioyd's mirror experiment (Figure.) a light wave emitted directly by the source (narrow slit) interferes with the wave reflected from a mirror . As a result, an interference fringe pattern is formed on the screen . The source and the mirror are separated by a distance . At a certain position of the source the fringe width on the screen was equal to , and after the source was moved away from the mirror plane by , the fringe width decreased times. Find the wavelength of light.