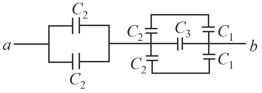
. If a potential difference of is applied across points and , then charge on the capacitor at steady state condition will be


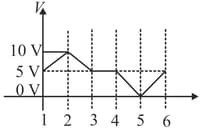
Important Questions on Capacitance
The versus -plot for six identical metal plates of cross-sectional area is as shown. The equivalent capacitance between and is (adjacent plates are placed at a separation )
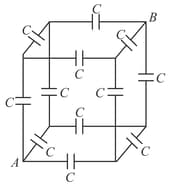
Each edge of the cube contains a capacitance . The equivalent capacitance between the points and will be
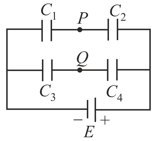
The potential difference between the points and in the adjoining circuit will be
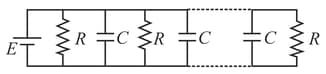
resistances each of resistance are joined with capacitors of capacity (each) and a battery of emf as shown in the figure. In steady state condition, ratio of charge stored in the first and last capacitor is:
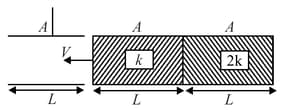
A parallel plate capacitor without any dielectric has capacitance . A dielectric slab is made up of two dielectric slabs of dielectric constants and and is of same dimensions as that of capacitor plates and both the parts are of equal dimensions arranged serially as shown. If this dielectric slab is introduced (dielectric enters first) in between the plates at a constant speed , then a variation of capacitance with time will be best represented by:
An isolated metallic object is charged in vacuum to a potential using a suitable source, its electrostatic energy being . It is then disconnected from the source and immersed in a large volume of dielectric with dielectric constant . The electrostatic energy of the sphere in the dielectric is:
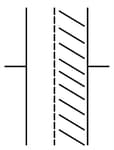
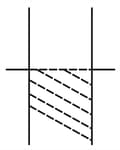
Consider a parallel plate capacitor. When half of the space between the plates is filled with some dielectric material of dielectric constant K as shown in below, the capacitance is . However, if the same dielectric material fills half the space as shown in , the capacitance is . Therefore, the ratio is