Re-write the equation for the hydrogenation of ethene using structural formulae.

Important Questions on Evidence
If bromine water is mixed with an alkene (for example, ethene) the bromine water goes from an orange–brown colour to colourless. This reaction is used to indicate the presence of a carbon-carbon double bond.
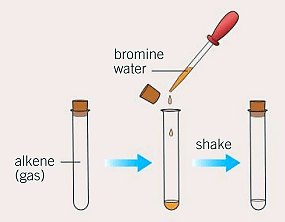
What reaction could be happening between bromine water and the alkene to cause the colour change?
Apply IUPAC nomenclature rules, state the name of the following compound:
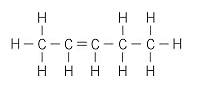
Apply IUPAC nomenclature rules, state the name of the following compound:
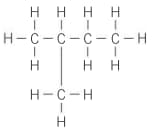
Apply IUPAC nomenclature rules, state the name of the following compound:
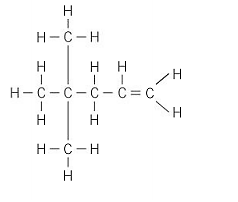
Apply IUPAC nomenclature rules, state the name of the following compound:
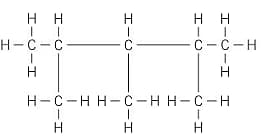
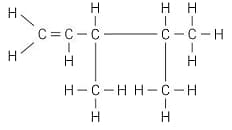
Apply IUPAC nomenclature rules, state the name of the following compound:
Catalytic cracking of paraffin:
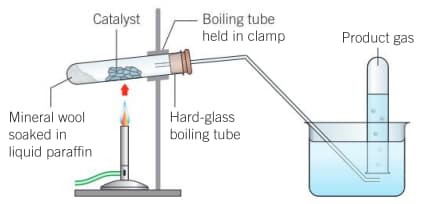
Procedure:
A mineral wool to a depth of in the bottom of the boiling tube. of liquid paraffin is dropped onto it using a dropping pipette. The boiling tube are clamped as shown in the diagram. 2–3 spatulas of the catalyst is placed in the centre of the tube and connect the tube. Six test tubes are filled with water and kept inverted in the water trough. The catalyst in the middle of the tube is strongly heated for a few minutes. When the catalyst is hot, the flame is passed back and forth over the liquid paraffin and catalyst to vaporize some of the liquid paraffin. Once the gas is released, the contents of the boiling tube is continuously heated to avoid suck-back. When a steady stream of gas bubbles are established, the six test tubes of gas are collected and sealed each full test tube with a bung. The first two test tubes are kept separate from the others. When gas collection is complete, the delivery tube is removed from the water by tilting or lifting the clamp stand, and then heating is stopped.
Question: Explain why the first two test tubes are discarded, and what is the main component in these samples?
Catalytic cracking of paraffin:
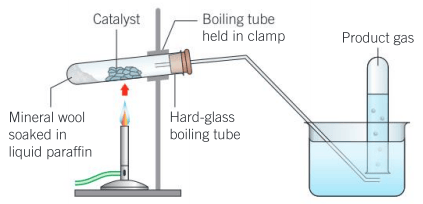
Procedure:
A mineral wool to a depth of in the bottom of the boiling tube. of liquid paraffin is dropped onto it using a dropping pipette. The boiling tube are clamped as shown in the diagram. spatulas of the catalyst is placed in the centre of the tube and connect the tube. Six test tubes are filled with water and kept inverted in the water trough. The catalyst in the middle of the tube is strongly heated for a few minutes. When the catalyst is hot, the flame is passed back and forth over the liquid paraffin and catalyst to vaporize some of the liquid paraffin. Once the gas is released, the contents of the boiling tube is continuously heated to avoid suck-back. When a steady stream of gas bubbles are established, the six test tubes of gas are collected and sealed each full test tube with a bung. The first two test tubes are kept separate from the others. When gas collection is complete, the delivery tube is removed from the water by tilting or lifting the clamp stand, and then heating is stopped.
Question: Describe the colour changes observed in the tests performed on the final two test tubes by using bromine water and potassium permanganate respectively.
