Calculate the Gibbs free energy change for the following reaction in . Values for are listed in the table.
Substance
(Write the value correctly upto two decimal places)

Important Questions on Energetics and Thermochemistry (AHL)
The lattice enthalpy of magnesium chloride can be calculated from the Born-Haber cycle shown in the figure.
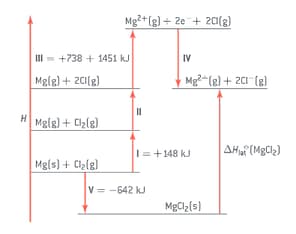
Identify the enthalpy changes labelled by I and V in the cycle.
The lattice enthalpy of magnesium chloride can be calculated from the Born-Haber cycle shown in figure.
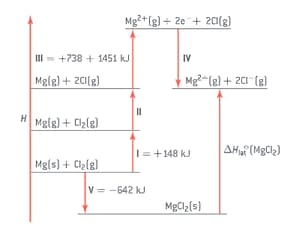
Use the ionization energies given in the cycle above and the data given here to calculate a value for the lattice enthalpy of magnesium chloride.
The lattice enthalpy of magnesium chloride can be calculated from the Born-Haber cycle shown in figure.
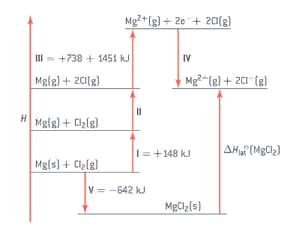
The theoretically calculated value for the lattice enthalpy of magnesium chloride is . Explain the difference between the theoretically calculated value and the experimental value.
The lattice enthalpy of magnesium chloride can be calculated from the Born-Haber cycle shown in figure.
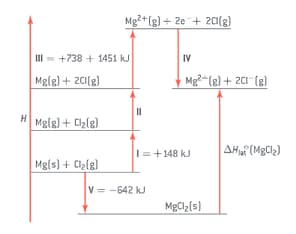
The experimental lattice enthalpy of magnesium oxide is . Explain why magnesium oxide has a higher lattice enthalpy than magnesium chloride.
The lattice enthalpy values for lithium fluoride and calcium fluoride are shown below.
Which of the following statements help(s) to explain why the value for lithium fluoride is less than that for calcium fluoride?
I) The ionic radius of lithium is less than that of calcium.
II) The ionic charge of lithium is less than that of calcium.
Which reaction occurs with the largest increase in entropy?
The and values for a certain reaction are both positive. Which statement is correct about the spontaneity of this reaction at different temperatures?
The following reaction is spontaneous only at temperatures above .
Which combination is correct for this reaction at ?
| A | |||
| B | |||
| C | |||
| D |
