Calculate the current in a gold wire of crosssectional area when the mean drift velocity of the electrons in the wire is . The electron number density for gold is .

Important Questions on Electric Current, Potential Difference and Resistance
A length of copper wire is joined in series to a length of silver wire of the same diameter. Both wires have a current in them when connected to a battery. Explain how the mean drift velocity of the electrons will change as they travel from the copper into the silver. Electron number densities:
Copper
Silver .
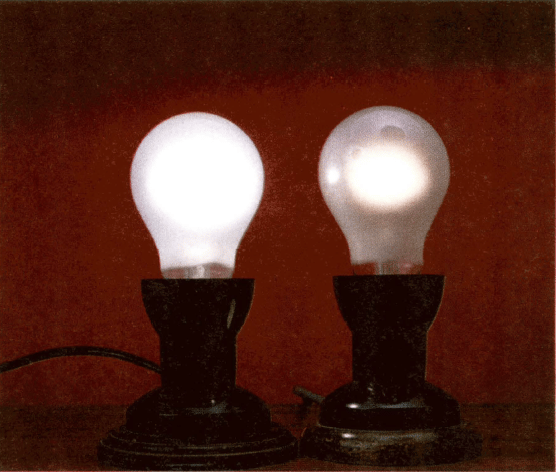
You can buy lamps of different brightness to fit in light fittings at home (Figure). A watt lamp glows more brightly than a watt lamp. Explain which of the lamps has the higher resistance.

(a ) Calculate the potential difference across a motor carrying a current of and having a resistance of .
In Figure the reading on the ammeter is and the reading on the voltmeter is Calculate the resistance of the metallic conductor.
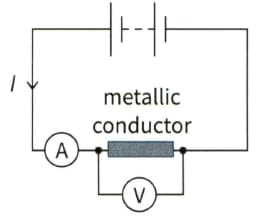
Connecting an ammeter and a voltmeter to determine the resistance of a metallic conductor in a circuit.
