MEDIUM
12th ICSE
IMPORTANT
Earn 100
Can a convex (converging) lens behave as a concave (diverging) lens in some situation? Give example.

Important Questions on Refraction of Light at Spherical Surfaces : Lenses
EASY
12th ICSE
IMPORTANT
A convex lens forms the image of the sun at a distance of . Where will the image be formed, if a lens of the same power but of double the aperture is used?
EASY
12th ICSE
IMPORTANT
A convex lens forms the image of the sun at a distance of . Where will the image be formed, if a lens of the same aperture but of double the power is used?
MEDIUM
12th ICSE
IMPORTANT
In the figure shown, is a point object placed in the air on the axis of a spherical surface of a glass block. is an incident ray. The direction of the refracted ray in the glass block is parallel to the principal axis . is the radius of the spherical surface. Use the formula to show that the object distance ; where and .
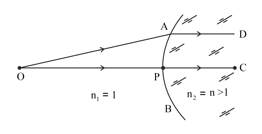
HARD
12th ICSE
IMPORTANT
A monochromatic ray of light is incident on a spherical refracting surface of refractive index . If and be the first and second focal lengths of the surface, show that .
HARD
12th ICSE
IMPORTANT
A thin lens has focal length and its aperture has diameter . It forms an image of intensity . What will be its focal length and image intensity if the central part of the lens is blocked up to diameter of the aperture by an opaque paper?
MEDIUM
12th ICSE
IMPORTANT
A convex lens and plane mirror are arranged as shown in figure. Position of the object pin is adjusted in such a way that the inverted image formed by the lens mirror combinations, coincides with the object pin . Explain how and when this happens.
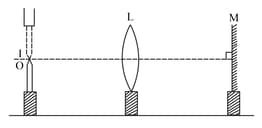
EASY
12th ICSE
IMPORTANT
A lens, whose radii of curvature are different, is forming the image of an object placed on its axis. If the lens is reversed, will the position of the image change?
MEDIUM
12th ICSE
IMPORTANT
The radii of curvature of both the surfaces of a convex lens are equal. Prove that the focal length of the lens will be equal to its radius of curvature if the refractive index of the material of the lens is .
