HARD
Earn 100
Can several identical charges be so arranged that the electric field and the potential both be zero at a point? Can several positive and negative charges be so arranged?
Important Questions on Electrostatic Potential and Capacitance
MEDIUM
There is a uniform electrostatic field in a region. The potential at various points on a small sphere centred at , in the region, is found to vary between the limits to . What is the potential at a point on the sphere whose radius vector makes an angle of with the direction of the field?
EASY
A metallic sphere is kept in between two oppositely charged plates. The most appropriate representation of the field lines is
EASY
An electron with an initial speed of is brought to rest by an electric field. The mass and charge of an electron are and , respectively. Identify the correct statement.
MEDIUM
Four point charges and are placed, one at each corner of the square. The relation between and for which the potential at the centre of the square is zero is
EASY
If potential(in ) in a region is expressed as , the electric field(in ) at point is
EASY
The diagrams below show regions of equipotential.
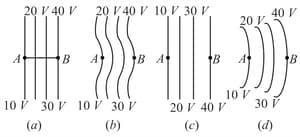
A positive charge is moved from to in each diagram.
MEDIUM
Two equal charges of magnitude each are placed at a distance apart. Their electrostatic energy is third charge is brought midway between these two charges. The electrostatic energy of the system is now?
EASY
The electric potential at a point in the - plane is given by
The electric field intensity at a distance from the origin varies as
MEDIUM
A charge Q is uniformly distributed over a long rod AB of length L as shown in the figure. The electric potential at the point O lying at a distance L from the end A is :
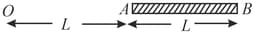
EASY
An electric field exists in a region of space. If the potential at the origin is taken to be zero then the potential at , is:
MEDIUM
A certain p-n junction having a depletion region of width was found to have a breakdown voltage of . If the width of the depletion region is reduced to during its production, then it can be used as a zener diode for voltage regulation of:
HARD
Four equal point charges each are placed in the plane at and . The work required to put a fifth charge at the origin of the coordinate system will be:
HARD
Consider a spherical shell of radius with a total charge uniformly spread on its surface (center of the shell lies at the origin ). Two point charge, are brought, one after the other, from far away and placed at respectively. Magnitude of the work done in this process is
HARD
A point particle of mass is moving along the -axis under a force described by the potential energy shown below. It is projected towards the right from the origin with a speed .
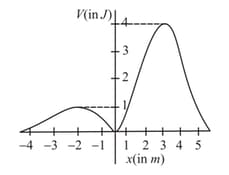
What is the minimum value of for which the particle will escape infinitely far away from the origin?
HARD
Some equipotential surfaces are shown. The electric field at any point is
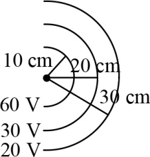
MEDIUM
A positive point charge is released from rest at a distance from a positive line charge with uniform charge density. The speed of the point charge, as a function of instantaneous distance from line charge, is proportional to
EASY
Assume that an electric field exists in space. Then the potential difference , where VO is the potential at the origin and VA the potential at x = 2 m is :
MEDIUM
Consider a cube of uniform charge density, . The ratio of the electrostatic potential at the center of the cube to that at one of the corners of the cube is,
MEDIUM
A charge is distributed over three concentric spherical shells of radii such that their surface charge densities are equal to one another.
The total potential at a point at distance from their common centre, where would be:
MEDIUM
When an -particle of mass moving with a undefined velocity bombards on a heavy nucleus of charge , its distance of the closest approach from the nucleus depends on as:

