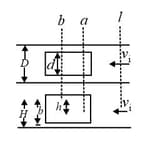
Canal effect. In the figure, shows an anchored barge that extends across a canal by distance and into the water by distance . The canal has a width , a water depth , and a uniform water-flow speed . Assume that the flow around the barge is uniform. As the water passes the bow, the water level undergoes a dramatic dip known as the canal effect. If the dip has depth , what is the water speed alongside the boat through the vertical cross-sections at (a) point and (b) point ? The erosion due to the speed increase is a common concern to hydraulic engineers.


Important Questions on Fluids
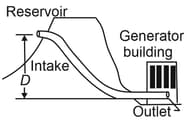
The intake in the figure has a cross-sectional area of and water flow at . At the outlet, the cross-sectional area is smaller than at the intake and the water flows out at into equipment. The pressure difference between intake and outlet is . What is the vertical distance ? (take )
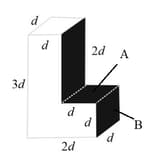
The L-shaped fish tank shown in the figure is filled with water and it's open at the top. If , what is the (total) force exerted by the water (a) on face and (b) on face ?
Lurking alligators. An alligator waits for prey by floating with only the top of its head exposed. So, the prey cannot easily see it. One way it can adjust the extent of sinking is by controlling the size of its lungs. Another way may be by swallowing stones (gastrolithes) that then reside in the stomach. In the figure shows a highly simplified model (a "rhombohedron gater") of mass that roams with its head partially exposed. The top head surface has area . If the alligator were to swallow stones with a total mass of of its body mass (a typical amount), how far would it sink ?