Choose the correct alternatives.

Important Questions on Rigid Body Dynamics II
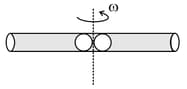
A smooth tube of certain mass is rotated in a gravity free space and released. The two balls, shown in the figure, move towards the ends of the tube. For the whole system, which of the following quantities are conserved.
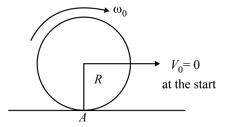
A disc of radius is rotating with an angular velocity about a horizontal axis. It is placed on a horizontal table. The coefficient of kinetic friction is ,
(a) What was the velocity of its centre of mass before being brought in contact with the table?
(b) What happens to the linear velocity of a point on its rim, when placed in contact with the table?
(c) What happens to the linear speed of the centre of mass, when the disc is placed in contact with the table?
(d) Which force is responsible for the effects in (b) and (c)?
(e) What condition should be satisfied for rolling to begin?
(f) Calculate the time taken for the rolling to begin.
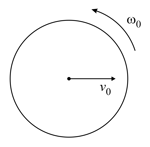
A uniform sphere of radius is projected on a horizontal surface with a velocity and simultaneously given a spin Consequently, the sphere experiences a combined motion. Due to the friction between the sphere and the horizontal surface, both translational and rotational motion will stop simultaneously. Then, what must be the magnitude and direction of initial spin ?
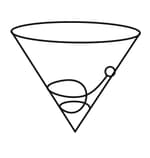
A ball is rolling without slipping in a spiral path down the inner surface of a hollow fixed cone whose axis is vertical. The work done by the inner surface of the cone on the ball is
As shown in the figure, is the point on a uniform disc is rolling with a uniform angular velocity on a fixed rough horizontal surface. The only forces acting on the disc are its weight and contact forces exerted by the horizontal surface. Which is the best graph that represents the magnitude of the acceleration of point on a uniform disc as a function of time?
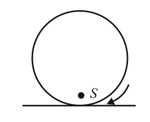
A disc of mass and radius is placed on a rough horizontal surface. A cue of mass hits the disc at a height from the axis passing through centre and parallel to the surface as shown. The cue stops and falls down after the impact. The disc starts its motion as:
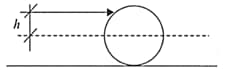
A cylinder moves with linear velocity to the right and angular velocity ω in the anticlockwise direction. The cylinder was initially at rest. The cylinder does not perform pure rolling and stops after some time. What will be the radius of the cylinder?
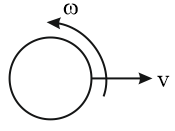
A solid sphere is set into rotation at an angular velocity and it is then, placed on a rough horizontal surface. The ratio of distances covered by rotational and translational motions up to the start of the pure rolling is (assume uniformly accelerated motion up to start of pure rolling):