Chris and his son are skating on an ice rink. Chris skates in a straight line at a speed of towards his son, who is stationary on the ice. When they meet Chris lifts his son up and they continue together at a speed of , still travelling in the same straight line. Chris has mass . Find the mass of his son.
Important Questions on Momentum
A ball of mass is moving at a speed of when it hits a stationary ball of mass . After the impact the first ball is stationary. Find the speed of the second ball.
A box of mass slides down a slope until it has reached a speed of It then travels at horizontally across a smooth floor until it bumps into a stationary crate. Immediately after the impact the box reverses its direction and travels at . The crate starts to travel at . Find the mass of the crate.
Two snooker balls are travelling towards one another in a straight line when they make a direct impact. Before the impact the first ball had speed and the second ball had speed . After the impact both balls have reversed their direction and each has speed . It is claimed that the balls are not both real snooker balls because they have different masses. Find the ratio of the masses of the balls.
Particles and , of masses and respectively, are at rest in a straight line on a smooth horizontal surface, with between and . is given an initial velocity of towards . After this impact rebounds with velocity and goes on to hit . After the second impact comes to rest. Find the speed of after the second impact.
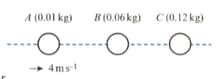
Three balls, and , of masses and , respectively, are at rest in a straight line on a smooth horizontal surface, with between and . is given an initial velocity of towards . When hits they coalesce and continue as a single object, , until they collide with . After this collision has velocity . Work out the final velocity of .
Jayne is performing in a show on ice. She is pushed onto the ice while sitting on a chair. The chair slides across the ice and Jayne then stands up and moves away from the chair. Jayne has speed when she is sitting on the chair and speed when she moves away from the chair. Jayne has mass and the chair has mass .
Find the velocity of the chair as Jayne moves away from it.
Jayne is performing in a show on ice. She is pushed onto the ice while sitting on a chair. The chair slides across the ice and Jayne then stands up and moves away from the chair. Jayne has speed when she is sitting on the chair and speed when she moves away from the chair. Jayne has mass and the chair has mass .
What modelling assumptions have you made?
A bean bag of mass is thrown at at a stationary target. The bean bag sticks to the target and they move of together at . Find the mass of the target.
