HARD
Earn 100
Consider a situation in which there is a Newtonian fluid between two long coaxial uniformly moving cylinders of radius and .
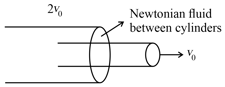

(a)Force per unit length required to keep the inner cylinder moving is
(b)Force per unit length required to keep the inner cylinder moving is
(c)Distance of the point from the axis at which speed of fluid is zero is
(d)Distance of the point from the axis at which speed of fluid is zero is
50% studentsanswered this correctly
Important Questions on Properties of Solid and Liquid
MEDIUM
EASY
MEDIUM
EASY
MEDIUM
HARD
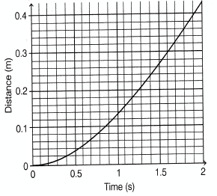
A steel ball is dropped in a viscous liquid. The distance of the steel ball from the top of the liquid is shown below. The terminal velocity of the ball is closest to
HARD
A raindrop with radius falls from a cloud at a height above the ground. Assume that the drop is spherical throughout its fall and the force of buoyance may be neglected, then the terminal speed attained by the raindrop is : [Density of water and Density of air Coefficient of viscosity of air
EASY
MEDIUM
HARD
HARD
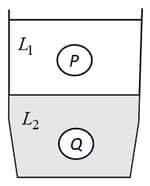
HARD
HARD
EASY
EASY
HARD
EASY
EASY
MEDIUM

