EASY
JEE Advanced
IMPORTANT
Earn 100
Consider an infinite line charge having uniform linear charge density and passing through the axis of a cylinder. What will be the effect on the flux passing through the curved surface if the portions of the line charge outside the cylinder is removed.
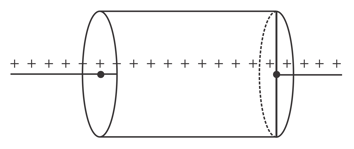

(a)Decreases
(b)Increases
(c)Remains same
(d)Cannot say
50% studentsanswered this correctly

Important Questions on Electric Flux and Gauss's Law
HARD
JEE Advanced
IMPORTANT
One-fourth of a sphere of radius is removed as shown in the figure. An electric field exists parallel to the plane. Find the flux through the remaining curved part.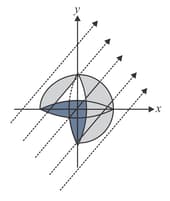
MEDIUM
JEE Advanced
IMPORTANT
A spherical shell of radius has a charge uniformly distributed over it. The force exerted by one half over the other half is
MEDIUM
JEE Advanced
IMPORTANT
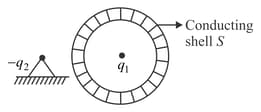
The negative charge is fixed while positive charge as well as the conducting sphere is free to move (refer figure). If the system is released from rest,
MEDIUM
JEE Advanced
IMPORTANT
A wire of linear charge density passes through a cuboid of length , breadth and height in such a manner that the flux through the cuboid is maximum. The position of the wire is now changed so that the flux through the cuboid is minimum. The ratio of maximum flux to minimum flux will be
EASY
JEE Advanced
IMPORTANT
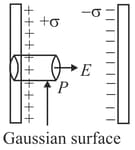
Consider the situation shown in figure. We find electric field at point using Gauss's law and it comes out to be . This electric field is due to
HARD
JEE Advanced
IMPORTANT
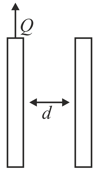
Two parallel conducting plates, each of area , are separated by a distance . Now, the left plate is given a positive charge . A positive charge of mass is released from a point near the left plate. Find the time taken by the charge to reach the right plate.
EASY
JEE Advanced
IMPORTANT
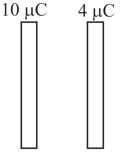
Two large plates are given the charges as shown in figure. Now, the left plate is earthed. Find the amount of charge that will flow from the earth to the plate.
HARD
JEE Advanced
IMPORTANT
The electric field in a region is given by .
Find the charge contained inside a cubical volume bounded by the surfaces and . Take , and .
