Consider the Figure and answer the following question.
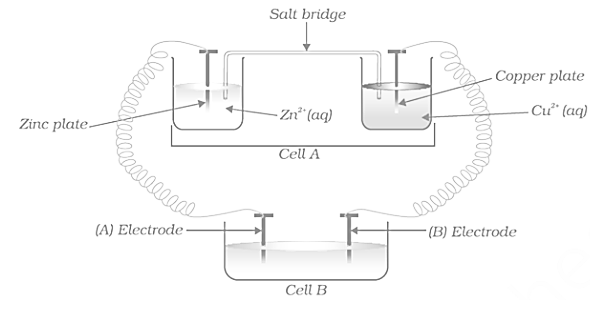
Cell has and Cell has which of the two cells or will act as an electrolytic cell. Which electrode reactions will occur in this cell?

Important Points to Remember in Chapter -1 - Electrochemistry from NCERT NCERT Exemplar Chemistry - Class 12 Solutions
(i) Electrochemical Cell: A device that converts chemical energy into electrical energy.
(ii) Anode: In electrochemical cells, the anode is the electrode at which oxidation takes place. It is the negative terminal.
(iii) Cathode: In electrochemical cells, the cathode is the electrode at which reduction takes place. It is the positive terminal.
2. Thermodynamic and electrochemical equations:
(i) EMF of the cell or .
(ii) Thermodynamic Efficiency of Cell: It is the ratio of the Gibb’s energy change to the enthalpy change of the cell reaction .
(iii) Electrochemical Series: Arrangement of various elements and electrode reactions in the increasing order of their reduction potentials.
(iv) Nernst Equation:
or
( is equiibrium constant for cell reaction)
(v)
(vi) Fuel Cell: A device which converts chemical energy of a fuel directly into electrical energy.
3. Conduction in electrolytes:
(i) Electrolyte : A substance that dissociates in solution to produce ions and hence conducts electricity in dissolved state or molten state.
(ii) Conductivity (k): Inverse of resistivity. Conductivity of a material in is its conductance when it is long and its area of cross section is . Its units are or or .
(iii) Molar Conductivity: Conductance of a solution containing one mole of the electrolyte, placed between two parallel electrodes one cm apart.
(iv)
(v) Molar conductivity of an electrolyte increases with dilution.
(vi) Limiting Molar Conductivity . It is the molar conductivity of electrolyte at infinite dilution.
(vii) Kohlrausch’s Law: The molar conductivity of an electrolyte at infinite dilution is equal to the sum of the ionic conductivities of the individual ions.
(viii) Degree of Dissociation : Fraction of total number of molecules that dissociates in solution.
(ix) Potential Gradient: It is the ratio of the potential applied across the electrodes to the distance between the electrodes.
(x) Electrolysis: The process of decomposition of electrolyte as a result of passage of electricity through its aqueous solution or through its molten state.
