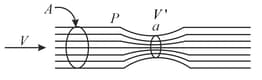
Consider the Venturi tube of figure. Let area equal Suppose the pressure at A is Compute the values of velocity at and velocity at that would make the pressure at equal to zero. Compute the corresponding volume flow rate if the diameter at is (The phenomenon at when falls to nearly zero is known as cavitation. The water vaporizes into small bubbles.)


Important Questions on Fluid Mechanics
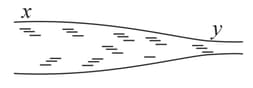
Water flows through a horizontal tube of variable cross-section (figure). The area of cross-section at and are and respectively. If of water enters per second through find
(i) the speed of the water at
(ii) the speed of the water at and
(iii) the pressure difference
Water flows through a horizontal tube of variable cross-section (figure). The area of cross-section at and are and respectively. If of water enters per second through find
(i) the speed of the water at
(ii) the speed of the water at and
(iii) the pressure difference
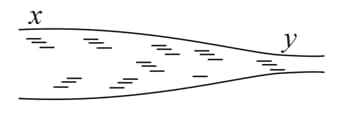
Suppose the tube in the previous problem is kept vertical with upward but the other conditions remain the same. The separation between the cross-section at and is . Repeat parts and of the previous problem. Take
Water flows through a horizontal tube of variable cross-section (figure). The area of cross-section at and are and respectively. If of water enters per second through find
(i) the speed of the water at
(ii) the speed of the water at and
(iii) the pressure difference
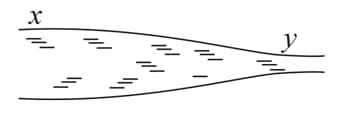
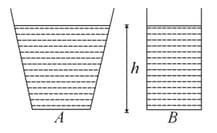
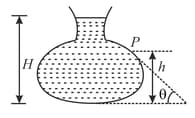
Figure here shows the vertical cross-section of a vessel filled with a liquid of density . The normal thrust per unit area on the walls of the vessel at a point , as shown, will be
Two vessels and of different shapes have the same base area and are filled with water up to the same height (see figure). The force exerted by water on the base is for vessel and for vessel The respective weights of the water-filled in vessels are and Then,