Consider the following data of the melting point of the first ten alkanes:
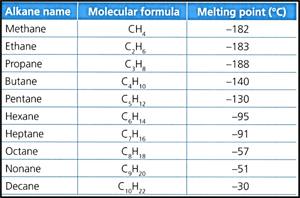
Identify, with reference to the information in the data table, the relationship between the length of alkane chain and its melting point.


Important Questions on Does Organic Chemistry Mean We Can Make Any Substance We Want?
Consider the following data of the melting point of the first ten alkanes:
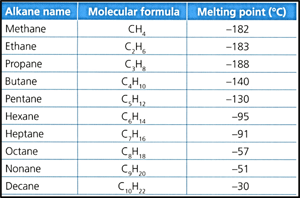
Identify, with reference to the information in the data table, what can you deduce about intermolecular attractions in decane compared to with those in methane.
The alkanes discussed in the text are either straight-chain or branched. However, there is a homologous series of alkanes known as cycloalkanes. The structure of cyclohexane () is shown below as a structural formula and a skeletal formula. Cyclohexane is a liquid at room temperature.
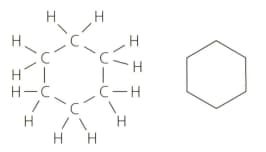
Deduce the general formula for the cycloalkanes and use it to predict the formulas for cycloheptane and cyclooctane.
The alkanes discussed in the text are either straight-chain or branched. However, there is a homologous series of alkanes known as cycloalkanes. The structure of cyclohexane () is shown below as a structural formula and a skeletal formula. Cyclohexane is a liquid at room temperature.
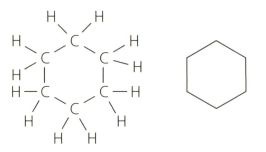
On an industrial scale cyclohexane is prepared by the hydrogenation of benzene (). Formulate an equation summarising this reaction.
Methanol, ethanol, propan--ol and butan--ol are all highly soluble in water, but pentan--ol is far less soluble and decan--ol is almost insoluble at .
A fresh ball of cotton wool is dipped into each of the alcohols listed above and rubbed across a piece of dark paper to produce a series of six ‘wet marks’. Predict, with reasons, the order in which the marks will evaporate to dryness.
Ethanedioic acid (commonly known as oxalic acid) is a poisonous substance found in rhubarb leaves. It has the following structural formula:
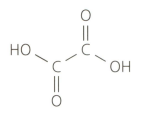
Suggest why ethanedioic acid is described as a dibasic acid in an aqueous solution.
Ethanedioic acid (commonly known as oxalic acid) is a poisonous substance found in rhubarb leaves. It has the following structural formula:
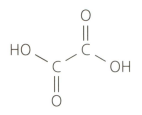
Deduce the molecular and empirical formulas of ethanedioic acid.
