EASY
Earn 100
Define aneuploidy. How is it different from polyploidy? Describe the individuals having following chromosomal disorders
(i) XXY
Important Questions on Principles of Inheritance and Variation
EASY
EASY
EASY
EASY
MEDIUM
HARD
MEDIUM
MEDIUM
EASY
An additional X-chromosome in a male
MEDIUM
HARD
(i) Haemophilia is a sex-linked recessive disease.
(ii) Down's syndrome is due to aneuploidy.
(iii) Phenylketonuria is an autosomal recessive gene disorder.
(iv) Sickle cell anaemia is an X-linked recessive gene disorder.
EASY
HARD
EASY
HARD
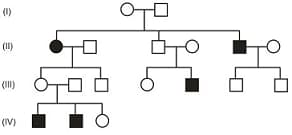
HARD
| Group I | Group II |
| P. Phenylketonuria | i. Melanin synthesis |
| Q. Albinism | ii. Conversion of Phenylalanine to Tyrosine |
| R. Homocystinuria | iii. Tyrosine degradation |
| S. Argininemia | iv. Methionine metabolism |
| v. Urea Synthesis |
MEDIUM
HARD
MEDIUM
Match the Column- I with Column - II
| Column - I | Column - II | ||
| i | Autosomal trisomy | p | Turner's Syndrome |
| ii | Allosomal trisomy | q | Mendelian disorder |
| iii | Allosomal Monosomy | r | Klinefelter's Syndrome |
| iv | Cystic fibrosis | s | Down's Syndrome |
EASY

