Define coefficient of viscosity.
Important Questions on Mechanical Properties of Fluids
A metal block of base area is placed on a table, as shown in figure. A liquid film of thickness is inserted between the block and the table. The block is pushed by a horizontal force of and moves with a constant speed. If the viscosity of the liquid is , the speed of block is ______ .

A flat plate of area is separated form a large plate by a layer of Glycerine thick. If the coefficient of viscosity of Glycerine is poise, the force required to keep the plate moving with a velocity of is
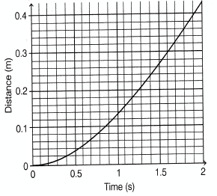
A steel ball is dropped in a viscous liquid. The distance of the steel ball from the top of the liquid is shown below. The terminal velocity of the ball is closest to
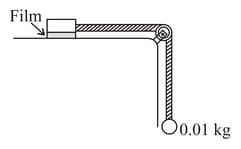
A metal block of Film area is connected to a mass is string that passes over a massless and frictionless pulley as shown figure. A liquid with a film thickness of is placed between the block and the table. When released the block moves to the right with a constant speed of . The coefficient of viscosity of the liquid is (Take )
If the equal and opposite deforming force are applied parallel to the cross-sectional area of the cylinder as shown in the figure, there is a relative displacement between the opposite faces of the cylinder.
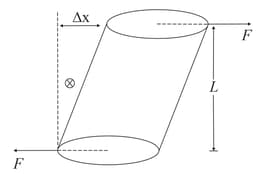
The ratio of to is known as
Glycerine flows steadily through a horizontal tube of length and radius . If the amount of glycerine collected per second at one end is , what is the pressure difference between the two ends of the tube? (Density of glycerine and viscosity of glycerine ). [You may also like to check if the assumption of laminar flow in the tube is correct].
(Choose from: Blood/Water/Emulsion paint)
In deriving Bernoulli’s equation, we equated the work done on the fluid in the tube to its change in the potential and kinetic energy. Do the dissipative forces become more important as the fluid velocity increases? Discuss qualitatively.

