EASY
Earn 100
Define freezing point of liquid.
Important Questions on Solutions
HARD
( for water ) is approximately:
(molar mass of and that of )
MEDIUM
Which of the following relations is correct?
MEDIUM
The freezing point of benzene decreases by on adding of acetic acid to of benzene. If acetic acid associates to form a dimer in benzene, then what is the percentage association of acetic acid in benzene?
MEDIUM
EASY
EASY
MEDIUM
MEDIUM
MEDIUM
The vapour pressure vs. temperature curve for a solution solvent system is shown below.
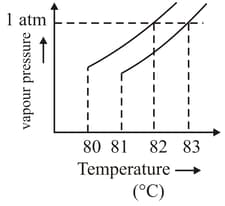
The boiling point of the solvent is _____°C.
MEDIUM
MEDIUM
Among the following, the option representing a change in the freezing point is
EASY
HARD
On dissolving of a non-volatile non-ionic solute to of benzene, its vapor pressure decreases from to The depression of freezing point of benzene (in ) upon addition of the solute is _______
(Given data: Molar mass and the molal freezing point depression constant of benzene are and respectively)
Give your answer up to three significant figures.
HARD
MEDIUM
(Assume complete dissociation of the electrolyte)
EASY
EASY
MEDIUM
EASY
MEDIUM
