Define range of molecular attraction.
Important Questions on Mechanical Properties of Fluids
If droplets of water of surface tension . having same radius each, combine to from a single drop. In the process the released surface energy is-
When water is filled carefully in a glass, one can fill it to a height above the rim of the glass due to the surface tension of water. To calculate just before water starts flowing, model the shape of the water above the rim as a disc of thickness having semicircular edges, as shown schematically in the figure. When the pressure of water at the bottom of this disc exceeds what can be withstood due to the surface tension, the water surface breaks near the rim and water starts flowing from there. If the density of water, its surface tension and the acceleration due to gravity are and respectively, the value of (in ) is ________.
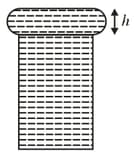
When a long glass capillary tube of radius is dipped in a liquid, the liquid rises to a height of within it. If the contact angle between the liquid and glass is close to , the surface tension of the liquid, is Millinewton . Write the value of .

