MEDIUM
Earn 100
Define thermal cracking.
Important Questions on Chemical Reactions of Organic Compounds
MEDIUM
Match columns A, B, and C suitably.
|
A Reactants |
B Products |
C Name of Reaction |
| Addition | ||
| Thermal cracking | ||
| Combustion | ||
| Substitution |
EASY
Organic compounds are obtained through different chemical reactions.
Complete the following reaction:
EASY
Two organic reactions are given below:
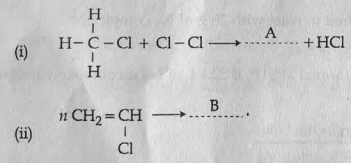
(a) Identify the products A and B.
(b) Which type of reaction is (i)?
(c) The product B has industrial values. Give its name and use.
EASY
Organic compounds are obtained through different chemical reactions.
What is the difference between substitution reactions and addition reactions?
EASY
EASY
Organic compounds are obtained through different chemical reactions.
Complete the following reaction:
EASY
MEDIUM
EASY
MEDIUM
MEDIUM
HARD
EASY
MEDIUM
MEDIUM
HARD
How does methane react with the chlorine, oxygen.
HARD
EASY
MEDIUM

