Determine the focal length of a concave spherical mirror which is manufactured in the form of a thin symmetric biconvex glass lens one of whose surfaces is silvered. The curvature radius of the lens surface is .

Important Questions on OPTICS
Figure illustrates an aligned system consisting of three thin lenses. The system is located in air. Determine,
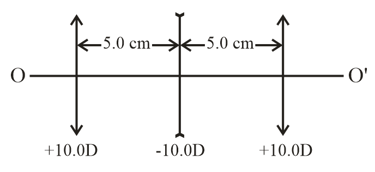
the position of the point of convergence of a parallel ray incoming from the left after passing through the system,
the distance between the first lens and a point lying on the axis to the left of the system, at which that point and its image are located symmetrically with respect to the lens system.
In Lioyd's mirror experiment (Figure.) a light wave emitted directly by the source (narrow slit) interferes with the wave reflected from a mirror . As a result, an interference fringe pattern is formed on the screen . The source and the mirror are separated by a distance . At a certain position of the source the fringe width on the screen was equal to , and after the source was moved away from the mirror plane by , the fringe width decreased times. Find the wavelength of light.
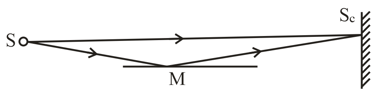
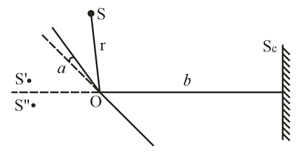
Figure illustrates the interference experiment with Fresnel mirrors. The angle between the mirrors is the distances from the mirrors' intersection line to the narrow slit and the screen are equal to and , respectively. The wavelength of light is . Find:
(a) the width of a fringe on the screen and the number of possible maxima;
(b) the shift of the interference pattern on the screen, when the slit is displaced by along the arc of radius , with centre at the point ;
(c) at what maximum width of the slit, the interference fringes on the screen are still observed sufficiently sharp.
(a) the width of a fringe on the screen and the number of possible maxima;
(b) the maximum width of the slit at which the fringes on the screen will be still observed sufficiently sharp.
A plane light wave with wavelength falls normally on the base of a biprism, made of glass with refracting angle . Behind the biprism there is a plane-parallel plate, with the space between them filled up with benzene . Find the width of a fringe on the screen placed behind this system.