MEDIUM
Earn 100
Different species are represented by and . Which of the following represents a community?
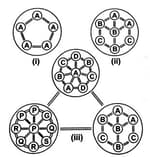
(a)(i)
(b)(ii)
(c)(iii)
(d)both (ii) and (iii)
50% studentsanswered this correctly
Important Questions on Use mathematical and/or computational representations to support explanations of factors that affect carrying capacity of ecosystems at different scales.
EASY
Life Sciences>Ecosystems: Interactions, Energy, and Dynamics>Use mathematical and/or computational representations to support explanations of factors that affect carrying capacity of ecosystems at different scales.>Interdependent Relationships in Ecosystems - Ecosystems have carrying capacities, which are limits to the numbers of organisms and populations they can support. These limits result from such factors as the availability of living and nonliving resources and from such challenges such as predation, competition, and disease. Organisms would have the capacity to produce populations of great size were it not for the fact that environments and resources are finite. This fundamental tension affects the abundance (number of individuals) of species in any given ecosystem.
HARD
Life Sciences>Ecosystems: Interactions, Energy, and Dynamics>Use mathematical and/or computational representations to support explanations of factors that affect carrying capacity of ecosystems at different scales.>Interdependent Relationships in Ecosystems - Ecosystems have carrying capacities, which are limits to the numbers of organisms and populations they can support. These limits result from such factors as the availability of living and nonliving resources and from such challenges such as predation, competition, and disease. Organisms would have the capacity to produce populations of great size were it not for the fact that environments and resources are finite. This fundamental tension affects the abundance (number of individuals) of species in any given ecosystem.
HARD
Life Sciences>Ecosystems: Interactions, Energy, and Dynamics>Use mathematical and/or computational representations to support explanations of factors that affect carrying capacity of ecosystems at different scales.>Interdependent Relationships in Ecosystems - Ecosystems have carrying capacities, which are limits to the numbers of organisms and populations they can support. These limits result from such factors as the availability of living and nonliving resources and from such challenges such as predation, competition, and disease. Organisms would have the capacity to produce populations of great size were it not for the fact that environments and resources are finite. This fundamental tension affects the abundance (number of individuals) of species in any given ecosystem.
| (a) | Earthworm | (p) | Pioneer species |
| (b) | Succession | (q) | Detrivore |
| (c) | Ecosystem service | (r) | Natality |
| (d) | Population growth | (s) | Pollination |
HARD
Life Sciences>Ecosystems: Interactions, Energy, and Dynamics>Use mathematical and/or computational representations to support explanations of factors that affect carrying capacity of ecosystems at different scales.>Interdependent Relationships in Ecosystems - Ecosystems have carrying capacities, which are limits to the numbers of organisms and populations they can support. These limits result from such factors as the availability of living and nonliving resources and from such challenges such as predation, competition, and disease. Organisms would have the capacity to produce populations of great size were it not for the fact that environments and resources are finite. This fundamental tension affects the abundance (number of individuals) of species in any given ecosystem.
1) The human liver fluke, a nematode parasite, depends on two intermediate hosts (a snail and a fish) to complete its life cycle.
2) The malarial parasite needs a vector (mosquito) to spread to other host organisms.
3) In case of brood parasitism, the eggs of parasitic birds (e.g., cuckoo) are not detected and removed from the nest because the parasite's eggs resemble the host's eggs in morphology and colour.
4) A population of frogs protected from all predators would decrease indefinitely.
MEDIUM
Life Sciences>Ecosystems: Interactions, Energy, and Dynamics>Use mathematical and/or computational representations to support explanations of factors that affect carrying capacity of ecosystems at different scales.>Interdependent Relationships in Ecosystems - Ecosystems have carrying capacities, which are limits to the numbers of organisms and populations they can support. These limits result from such factors as the availability of living and nonliving resources and from such challenges such as predation, competition, and disease. Organisms would have the capacity to produce populations of great size were it not for the fact that environments and resources are finite. This fundamental tension affects the abundance (number of individuals) of species in any given ecosystem.
EASY
Life Sciences>Ecosystems: Interactions, Energy, and Dynamics>Use mathematical and/or computational representations to support explanations of factors that affect carrying capacity of ecosystems at different scales.>Interdependent Relationships in Ecosystems - Ecosystems have carrying capacities, which are limits to the numbers of organisms and populations they can support. These limits result from such factors as the availability of living and nonliving resources and from such challenges such as predation, competition, and disease. Organisms would have the capacity to produce populations of great size were it not for the fact that environments and resources are finite. This fundamental tension affects the abundance (number of individuals) of species in any given ecosystem.
HARD
Life Sciences>Ecosystems: Interactions, Energy, and Dynamics>Use mathematical and/or computational representations to support explanations of factors that affect carrying capacity of ecosystems at different scales.>Interdependent Relationships in Ecosystems - Ecosystems have carrying capacities, which are limits to the numbers of organisms and populations they can support. These limits result from such factors as the availability of living and nonliving resources and from such challenges such as predation, competition, and disease. Organisms would have the capacity to produce populations of great size were it not for the fact that environments and resources are finite. This fundamental tension affects the abundance (number of individuals) of species in any given ecosystem.
| Column-I | Column-II | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Saprophyte | Symbiotic association of fungi with plant roots | ||
| Parasite | Decomposition of dead organic materials | ||
| Lichens | Living on living plants | ||
| Mycorrhiza | Symbiotic association of algae and fungi |
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
MEDIUM
Life Sciences>Ecosystems: Interactions, Energy, and Dynamics>Use mathematical and/or computational representations to support explanations of factors that affect carrying capacity of ecosystems at different scales.>Interdependent Relationships in Ecosystems - Ecosystems have carrying capacities, which are limits to the numbers of organisms and populations they can support. These limits result from such factors as the availability of living and nonliving resources and from such challenges such as predation, competition, and disease. Organisms would have the capacity to produce populations of great size were it not for the fact that environments and resources are finite. This fundamental tension affects the abundance (number of individuals) of species in any given ecosystem.
If resources are limited
If two species occupy different niches
If resource partitioning takes place between two species
If two species occupy identical niche
EASY
Life Sciences>Ecosystems: Interactions, Energy, and Dynamics>Use mathematical and/or computational representations to support explanations of factors that affect carrying capacity of ecosystems at different scales.>Interdependent Relationships in Ecosystems - Ecosystems have carrying capacities, which are limits to the numbers of organisms and populations they can support. These limits result from such factors as the availability of living and nonliving resources and from such challenges such as predation, competition, and disease. Organisms would have the capacity to produce populations of great size were it not for the fact that environments and resources are finite. This fundamental tension affects the abundance (number of individuals) of species in any given ecosystem.
EASY
Life Sciences>Ecosystems: Interactions, Energy, and Dynamics>Use mathematical and/or computational representations to support explanations of factors that affect carrying capacity of ecosystems at different scales.>Interdependent Relationships in Ecosystems - Ecosystems have carrying capacities, which are limits to the numbers of organisms and populations they can support. These limits result from such factors as the availability of living and nonliving resources and from such challenges such as predation, competition, and disease. Organisms would have the capacity to produce populations of great size were it not for the fact that environments and resources are finite. This fundamental tension affects the abundance (number of individuals) of species in any given ecosystem.
EASY
Life Sciences>Ecosystems: Interactions, Energy, and Dynamics>Use mathematical and/or computational representations to support explanations of factors that affect carrying capacity of ecosystems at different scales.>Interdependent Relationships in Ecosystems - Ecosystems have carrying capacities, which are limits to the numbers of organisms and populations they can support. These limits result from such factors as the availability of living and nonliving resources and from such challenges such as predation, competition, and disease. Organisms would have the capacity to produce populations of great size were it not for the fact that environments and resources are finite. This fundamental tension affects the abundance (number of individuals) of species in any given ecosystem.
In the following equation of Verhulst - Pearl logistic growth, the letter denotes ___ .
MEDIUM
Life Sciences>Ecosystems: Interactions, Energy, and Dynamics>Use mathematical and/or computational representations to support explanations of factors that affect carrying capacity of ecosystems at different scales.>Interdependent Relationships in Ecosystems - Ecosystems have carrying capacities, which are limits to the numbers of organisms and populations they can support. These limits result from such factors as the availability of living and nonliving resources and from such challenges such as predation, competition, and disease. Organisms would have the capacity to produce populations of great size were it not for the fact that environments and resources are finite. This fundamental tension affects the abundance (number of individuals) of species in any given ecosystem.
EASY
Life Sciences>Ecosystems: Interactions, Energy, and Dynamics>Use mathematical and/or computational representations to support explanations of factors that affect carrying capacity of ecosystems at different scales.>Interdependent Relationships in Ecosystems - Ecosystems have carrying capacities, which are limits to the numbers of organisms and populations they can support. These limits result from such factors as the availability of living and nonliving resources and from such challenges such as predation, competition, and disease. Organisms would have the capacity to produce populations of great size were it not for the fact that environments and resources are finite. This fundamental tension affects the abundance (number of individuals) of species in any given ecosystem.
The shape of the pyramids reflects the growth status of the population. Identify the type of age pyramid represented below for human population.

EASY
Life Sciences>Ecosystems: Interactions, Energy, and Dynamics>Use mathematical and/or computational representations to support explanations of factors that affect carrying capacity of ecosystems at different scales.>Interdependent Relationships in Ecosystems - Ecosystems have carrying capacities, which are limits to the numbers of organisms and populations they can support. These limits result from such factors as the availability of living and nonliving resources and from such challenges such as predation, competition, and disease. Organisms would have the capacity to produce populations of great size were it not for the fact that environments and resources are finite. This fundamental tension affects the abundance (number of individuals) of species in any given ecosystem.
EASY
Life Sciences>Ecosystems: Interactions, Energy, and Dynamics>Use mathematical and/or computational representations to support explanations of factors that affect carrying capacity of ecosystems at different scales.>Interdependent Relationships in Ecosystems - Ecosystems have carrying capacities, which are limits to the numbers of organisms and populations they can support. These limits result from such factors as the availability of living and nonliving resources and from such challenges such as predation, competition, and disease. Organisms would have the capacity to produce populations of great size were it not for the fact that environments and resources are finite. This fundamental tension affects the abundance (number of individuals) of species in any given ecosystem.
EASY
Life Sciences>Ecosystems: Interactions, Energy, and Dynamics>Use mathematical and/or computational representations to support explanations of factors that affect carrying capacity of ecosystems at different scales.>Interdependent Relationships in Ecosystems - Ecosystems have carrying capacities, which are limits to the numbers of organisms and populations they can support. These limits result from such factors as the availability of living and nonliving resources and from such challenges such as predation, competition, and disease. Organisms would have the capacity to produce populations of great size were it not for the fact that environments and resources are finite. This fundamental tension affects the abundance (number of individuals) of species in any given ecosystem.
MEDIUM
Life Sciences>Ecosystems: Interactions, Energy, and Dynamics>Use mathematical and/or computational representations to support explanations of factors that affect carrying capacity of ecosystems at different scales.>Interdependent Relationships in Ecosystems - Ecosystems have carrying capacities, which are limits to the numbers of organisms and populations they can support. These limits result from such factors as the availability of living and nonliving resources and from such challenges such as predation, competition, and disease. Organisms would have the capacity to produce populations of great size were it not for the fact that environments and resources are finite. This fundamental tension affects the abundance (number of individuals) of species in any given ecosystem.
Read the following data carefully
| Parameter | Values |
| Initial population of lions | |
| Number of new births in one year | |
| Number of deaths in one year |
Imagine the lion population grows logistically where the carrying capacity is Then the per capita birth rate, per capita death rate, intrinsic rate of natural increase, increase or decrease in population during the unit time period are respectively
EASY
Life Sciences>Ecosystems: Interactions, Energy, and Dynamics>Use mathematical and/or computational representations to support explanations of factors that affect carrying capacity of ecosystems at different scales.>Interdependent Relationships in Ecosystems - Ecosystems have carrying capacities, which are limits to the numbers of organisms and populations they can support. These limits result from such factors as the availability of living and nonliving resources and from such challenges such as predation, competition, and disease. Organisms would have the capacity to produce populations of great size were it not for the fact that environments and resources are finite. This fundamental tension affects the abundance (number of individuals) of species in any given ecosystem.
EASY
Life Sciences>Ecosystems: Interactions, Energy, and Dynamics>Use mathematical and/or computational representations to support explanations of factors that affect carrying capacity of ecosystems at different scales.>Interdependent Relationships in Ecosystems - Ecosystems have carrying capacities, which are limits to the numbers of organisms and populations they can support. These limits result from such factors as the availability of living and nonliving resources and from such challenges such as predation, competition, and disease. Organisms would have the capacity to produce populations of great size were it not for the fact that environments and resources are finite. This fundamental tension affects the abundance (number of individuals) of species in any given ecosystem.
EASY
Life Sciences>Ecosystems: Interactions, Energy, and Dynamics>Use mathematical and/or computational representations to support explanations of factors that affect carrying capacity of ecosystems at different scales.>Interdependent Relationships in Ecosystems - Ecosystems have carrying capacities, which are limits to the numbers of organisms and populations they can support. These limits result from such factors as the availability of living and nonliving resources and from such challenges such as predation, competition, and disease. Organisms would have the capacity to produce populations of great size were it not for the fact that environments and resources are finite. This fundamental tension affects the abundance (number of individuals) of species in any given ecosystem.

