MEDIUM
Earn 100
Distinguish between the true and false fruits.
Important Questions on Sexual Reproduction in Flowering Plants
MEDIUM
HARD
EASY
EASY
EASY
MEDIUM
MEDIUM
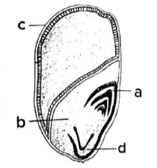
In the given diagram identify the parts labelled as a, b, c and d.
EASY
EASY
EASY
EASY
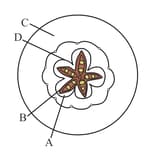
Which part of the fruit, labelled in the given figure makes it a false fruit?
MEDIUM
EASY
MEDIUM
MEDIUM
A. The tip of embryonic axis emerges out first during seed germination is called rachis.
B. In Artocarpus integrifolia, the fruit type is syconus, where the edible part is succulent perianth.
C. In Pyrus malus, the edible part is false fruit.
D. Pepo fruit is developed from tricarpellary, unilocular inferior ovary.
MEDIUM
EASY
EASY
MEDIUM
EASY
Match the types of fruits presented in List-I with the name of the plants given in the List-II.
| List- | List- | ||
| (A) | Schizocarpic fiuit | (I) | Mustard |
| (B) | False fruit | (II) | Acacia |
| (C) | Parthenocarpic fruit | (III) | Strawberry |
| (D) | Dry fruit | (IV) | Banana |
| (V) | Cotton |
The correct match is:

