Draw an enthalpy cycle as an energy level diagram showing the relationship between lattice energy, enthalpy change of solution and enthalpy change of hydration for barium sulfate. is very endothermic.

Important Questions on Lattice Energy
The table shows the enthalpy changes needed to calculate the lattice energy of potassium oxide, .
| Type of enthalpy change | Value of enthalpy change/ |
| first ionisation energy of potassium | |
| first electron affinity of oxygen | |
| second electron affinity of oxygen | |
| enthalpy change of formation of | |
| enthalpy change of atomisation of potassium | |
| enthalpy change of atomisation of oxygen |
Copy the incomplete Born-Haber cycle shown below. On the lines A to E of your copy of the Born-Haber cycle, write the correct symbols relating to potassium and oxygen.
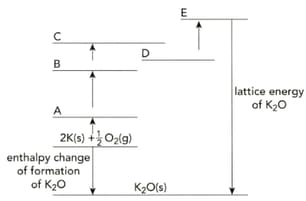
The table shows the enthalpy changes needed to calculate the lattice energy of potassium oxide, .
| Type of enthalpy change | Value of enthalpy change/ |
| first ionisation energy of potassium | |
| first electron affinity of oxygen | |
| second electron affinity of oxygen | |
| enthalpy change of formation of | |
| enthalpy change of atomisation of potassium | |
| enthalpy change of atomisation of oxygen |
Use the data in the table above to calculate the lattice energy of potassium oxide.
The table shows the enthalpy changes needed to calculate the lattice energy of potassium oxide, .
| Type of enthalpy change | Value of enthalpy change/ |
| first ionisation energy of potassium | |
| first electron affinity of oxygen | |
| second electron affinity of oxygen | |
| enthalpy change of formation of | |
| enthalpy change of atomisation of potassium | |
| enthalpy change of atomisation of oxygen |
Explain why the second electron affinity of oxygen has a positive value.
Define the term first ionisation energy.
Define the term enthalpy change of atomisation.
Draw and label a Born-Haber cycle to calculate the lattice energy of sodium chloride.
